- 44 –
No.JXC
※
-OMY0002
8. Perations
8.1 Return to origin position
After inputting the set data, it is necessary to perform a return to origin (to establish the origin point) before
starting the positioning or pushing operation (to ensure the position of origin).
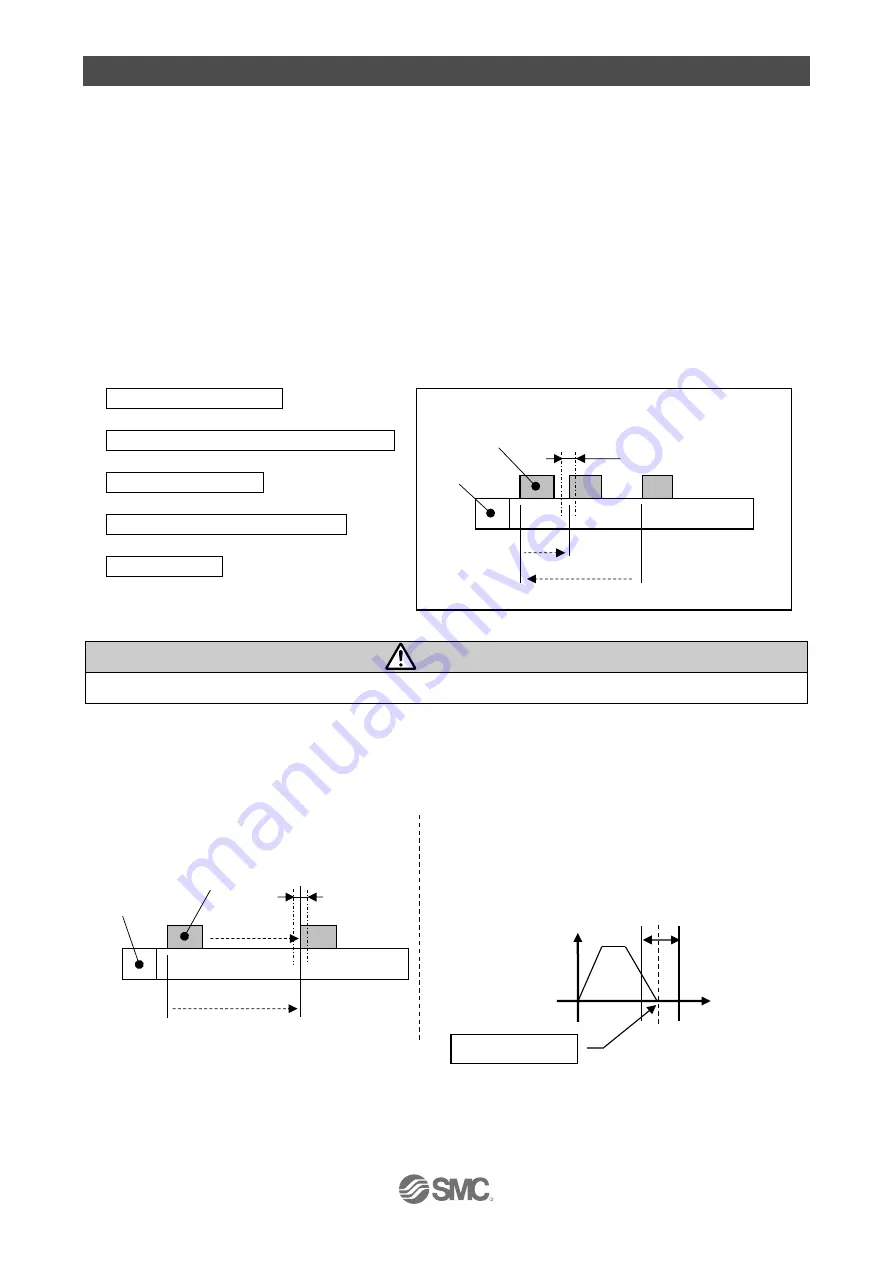
■Return to origin operation
The actuator moves in the return to origin direction (* this direction is dependent on the actuator) from the
initial position at the moment of power ON. Refer to (1) in the figure below.
When the actuator reaches the end of travel limit it pauses for a short time. The controller recognizes the
position as the end of travel limit of the actuator. Then, the actuator moves at a low speed in the direction
opposite to the return to origin direction: Refer to (2) in the figure below.
The position after the travel becomes the origin.
Return to origin signal
↓
Move in the return to origin direction
↓
Stop the movement
↓
Move in the opposite direction
↓
Origin position
Caution
This direction is dependent on the electric actuator.
8.2 Positioning operation
Step data "Pushing force" is 0.
The electric actuator moves to the target position specified by the step data "Position".
●Positioning operation (Example) ● Positioning operation [Speed/ Position] (Example)
Load
Motor
Origin position
(Example) Return to origin operation
Electric actuator
electric
Actuator
end
Origin position
Initial
position
(1)
(2)
Basic parameter
"Def in position"
Load
Motor
Electric actuator
Step data
"Speed"
Step data
"In position"
Target position
→Step data "Position"
Target position
Positioning range
(In position)
Position
Speed
















































