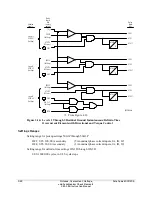
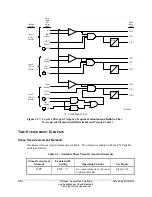
3-36
Distance, Overcurrent, Voltage,
Date Code 20011205
and Synchronism Check Elements
SEL-311B Instruction Manual
S
YNCHRONISM
C
HECK
E
LEMENTS
Enable the two single-phase synchronism check elements by making the enable setting:
E25 = Y
Figure 2.5 and Figure 2.6 in
Section 2: Installation
show examples where synchronism check
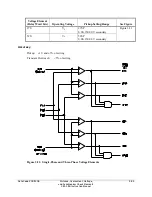
can be applied. Synchronism check voltage input VS is connected to a potential transformer
secondary on one side of the circuit breaker, on any desired phase or between any two phases.
The other synchronizing phase (VA, VB, VC, VAB, VBC, or VCA) taken from a potential
transformer secondary on the other side of the circuit breaker is selected by setting SYNCP.
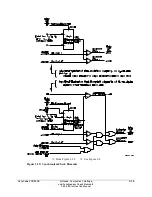
The two synchronism check elements use the same voltage magnitude window (to ensure healthy
voltage) and slip frequency settings (see Figure 3.24). They have separate angle settings (see
Figure 3.25).
Fixed Angle Synchronism Check
To implement a simple fixed-angle synchronism check scheme, set TCLOSD = OFF and 25SF =
0.500. With these settings, the synchronism check is performed as described in the top of Figure
3.25.
If there is the possibility of a high slip frequency, exercise caution if synchronism check elements
25A1 or 25A2 are used to close a circuit breaker. A high slip frequency and a slow breaker close
could result in closing the breaker outside the synchronism check window. Qualify the breaker
close command with a time delay, such as:
SV1 = 25A1
CL = CC + SV1T
Set SV1PU with enough pickup delay to insure that the slip frequency is low enough for the
circuit breaker to close within the synchronism check window.
Dynamic Synchronism Check
The remainder of this discussion assumes TCLOSD is not set to OFF. With TCLOSD not set to
OFF, the synchronism check is performed as described in either the top or bottom of Figure 3.25,
depending on the slip frequency.
If the voltages are static (voltages not slipping with respect to one another), the two synchronism
check elements operate as shown in the top of Figure 3.25. The angle settings are checked for
synchronism check closing.
If the voltages are not static (voltages slipping with respect to one another), the two synchronism
check elements operate as shown in the bottom of Figure 3.25. The angle difference is
compensated by breaker close time, and the breaker is ideally closed at a zero degree phase angle
difference, to minimize system shock.
These synchronism check elements are explained in detail in the following text.
Содержание SEL-311B
Страница 6: ......
Страница 8: ......
Страница 10: ......
Страница 24: ......
Страница 26: ......
Страница 122: ......
Страница 124: ......
Страница 138: ......
Страница 168: ......
Страница 172: ......
Страница 254: ......
Страница 282: ......
Страница 306: ......
Страница 348: ......
Страница 364: ......
Страница 366: ......
Страница 448: ......
Страница 460: ......
Страница 466: ......
Страница 476: ......
Страница 482: ......
Страница 494: ......
Страница 500: ......
Страница 522: ......
Страница 526: ......
Страница 528: ......
Страница 534: ......
Страница 536: ......
Страница 550: ......
Страница 570: ......
Страница 586: ......
Страница 600: ......