Raisecom
ISCOM2600G-HI (A) Series Configuration Guide
10 Security
Raisecom Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd.
431
10.7 802.1x
10.7.1 Introduction
802.1x, based on IEEE 802.1x, is a VLAN-based network access control technology. It is
used to solve authentication and security problems for LAN users.
It is used to authenticate and control access devices at the physical later of the network device.
It defines a point-to-point connection mode between the device interface and user devices.
User devices, connected to the interface, can access resources in the LAN if they are
authenticated. Otherwise, they cannot access resources in the LAN through the switch.
802.1x structure
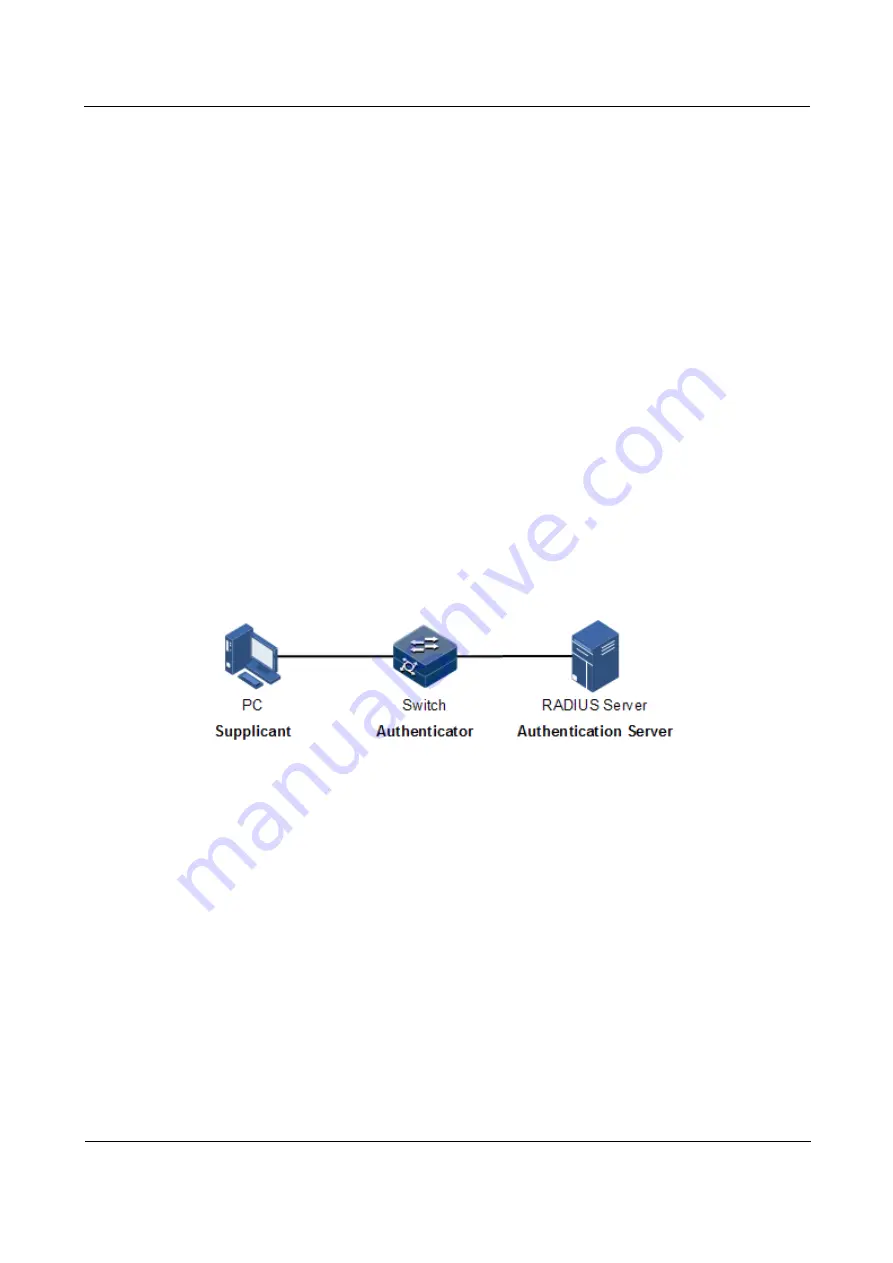
As shown in Figure 10-7, 802.1x authentication uses Client/Server mode, including the
following 3 parts:
Supplicant: a user-side device installed with the 802.1x client software (such as Windows
XP 802.1x client), such as a PC
Authenticator: an access control device supporting 802.1x authentication, such as a
switch
Authentication Server: a device used for authenticating, authorizing, and accounting
users. Generally, the RADIUS server is taken as the 802.1x authentication server.
Figure 10-7
802.1x structure
Interface access control modes
The authenticator uses the authentication server to authenticate clients that need to access the
LAN and controls interface authorized/ unauthorized status through the authentication results.
You can control the access status of an interface by configuring access control modes on the
interface. 802.1x authentication supports the following 3 interface access control modes:
Protocol authorized mode (auto): the protocol state machine determines the authorization
and authentication results. Before clients are successfully authenticated, only EAPoL
packets are allowed to be received and sent. Users are disallowed to access network
resources and services provided by the switch. If clients are authorized, the interface is
switched to the authorized state, allowing users to access network resources and services
provided by the switch.
Force interface authorized mode (authorized-force): the interface is in authorized state,
allowing users to access network resources and services provided by the switch without
being authorized and authenticated.
Force interface unauthorized mode (unauthorized-force): the interface is in unauthorized
mode. Users are disallowed to access network resources and services provided by the
switch; in other words, users are disallowed to be authenticated.






























