Motion Control Units
Product Specifications
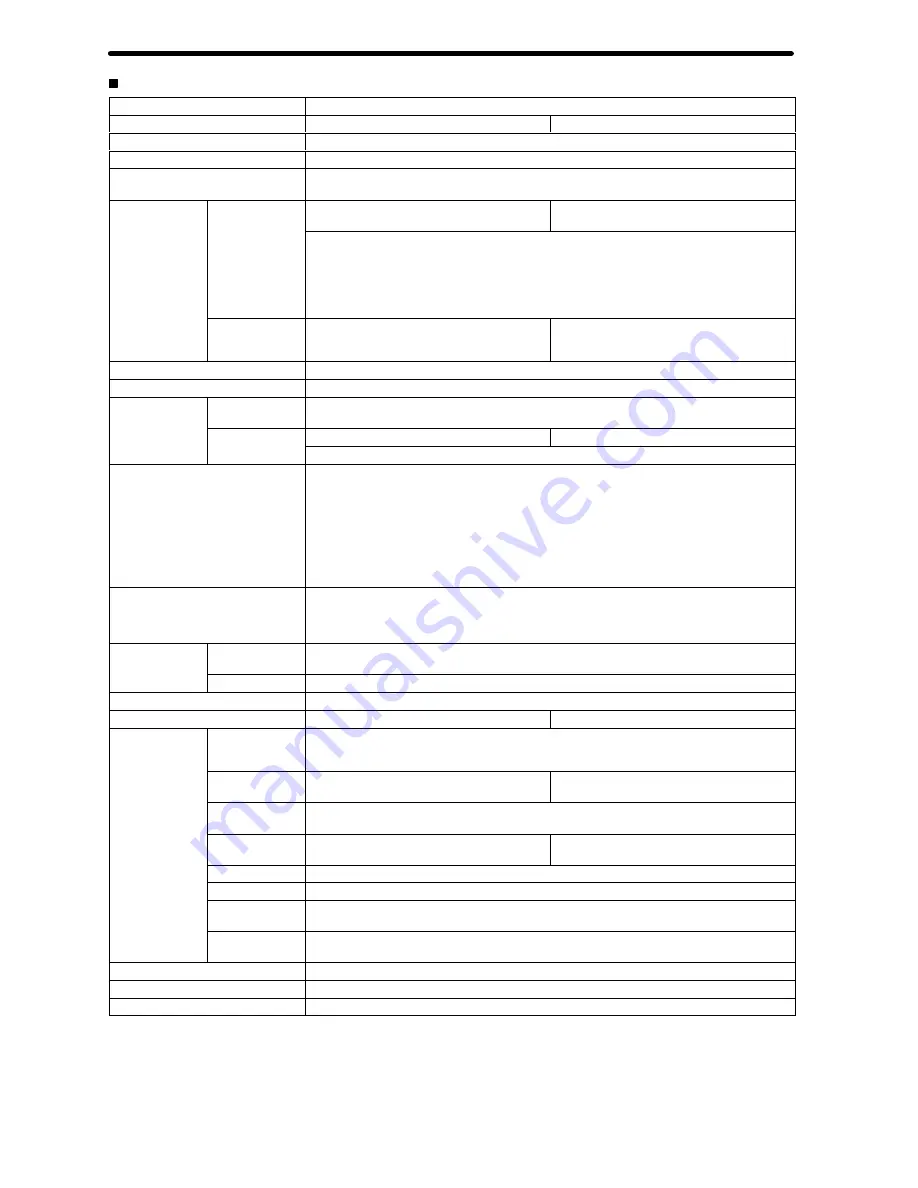
4
Specifications
Item
Specifications
Model
CS1W-MC221
CS1W-MC421
Applicable PC
CS1 Series
Type of Unit
CS1 Special I/O Unit
Backplanes on which MC Unit can
be mounted
CPU Backplane or CS1 Expansion I/O Backplane (See note 1.)
Method for data
transfer with
CPU U it
Words allocated
to Special I/O
U it i CIO
30 words/Unit (uses 3 unit numbers.) (See
note 2.)
50 words/Unit (uses 5 unit numbers.) (See
note 2.)
CPU Unit
Units in CIO
Area
CPU Unit to MC Unit:
Commands: G-language program execution/stop, origin search, manual operation, etc.
Data transfer: Position data, acceleration/ deceleration data, etc.
MC Unit to CPU Unit:
Status: Positioning completed, zones, busy flag, etc.
Monitor data: Present position, error codes, M codes, etc.
Words allocated
to Special I/O
Units in DM Area
Not used.
Not used.
Controlled Driver
Analog input servodriver (Example: OMRON OMNUC H, M, or U Series)
Built-in program language
G language (Started by receiving a start command from the CPU Unit ladder diagram program.)
Control
Control method
Speed reference voltage output-type semi-closed loop system, using incremental and absolute
encoder inputs.
Number of
t ll d
2 max.
4 max.
u be o
controlled axes
Multitasking can be used to execute independent operating modes and programs for each axis.
Automatic/Manual Mode (for each
task)
Automatic Mode: Mode for executing MC program created in G language.
Manual Mode: Mode for executing manual commands from CPU Unit (PC interface area) or
Teaching Box.
Note: The Automatic or Manual Mode is set according to the PC interface area of the CPU Unit.
There are a total of 11 Automatic Mode commands, including origin search, reference origin
return, JOG, and error reset.
The operation cycle is started in Automatic Mode through dedicated bits in the CPU Unit or from
the Teaching Box.
Encoder interface
Line receiver input; maximum response frequency: 500 kp/s (before multiplication)
Pulse ratio: Select 1, 2, or 4
Note: The applicable absolute encoder is the OMRON OMNUC U Series.
Control unit
Minimum setting
unit
1, 0.1, 0.01, 0.001, 0.0001
Units
mm, inch, degree, pulse (There is no unit conversion function.)
Maximum command value
–39,999,999 to +39,999,999 (When the minimum setting unit is 1.)
Number of controlled axes
2 axes max.
4 axes max.
Positioning
operations
PTP
(independent)
control
Execution by independent programs, operating modes for each axis.
Linear
interpolation
2 axes max
4 axes max.
Circular
interpolation
Circular interpolation for a maximum of two axes on a plane.
Helical circular
interpolation
---
Circular interpolation for a maximum of two
axes on a plane + one axis for feed control
Traverse function
Traverse operation for two axes
Speed control
Speed control for each axis
Unlimited Feed
Mode
Axis feeding can be executed with no limit.
Interrupt feeding
Feeding a fixed distance after an interrupt input, for each axis. (Positioning with no interrupt
input signals is also possible.)
Speed reference
1 pps to 2,000 kp/s (when ratio is 4)
Acceleration/deceleration curve
Trapezoidal or S-curve
Acceleration/deceleration time
Individual acceleration/deceleration settings possible: 0 to 100,000 ms (2-ms increments)
Note:
1. The MC Unit must be mounted to the CPU Rack to use D codes. D codes will not be sent to the CPU Unit if the MC Unit is mounted to
a CS1 Expansion Rack.
2. The number of MC Units that can be mounted under one CPU Unit must be determined based on the maximum number of Special
I/O Units that can be allocated words in the CPU Unit, the power supply capacity on the CPU or CS1 Expansion Rack, and the
current consumption of the Units mounted to the Rack. Refer to the CPU Unit’s operation manual for details on calculation methods.






































