Nexland ISB SOHO: Interface Screens
26
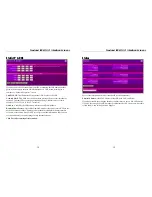
Routing Table Data
An entry in the routing table is required for each LAN segment on your Network. An
entry is required so any other segment attached to this device can share data back and
forth. The data in the Routing Table is as follows.
Click
Add
to Add a new entry
Click
Delete
to Delete the entry shown and free up ISB memory
Click
Update
if you have changed the entry shown
Click
Clear
Form before Adding a new entry
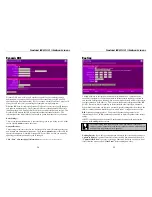
Router Configuration
It is essential that all IP packets for devices not on the local network be passed through
the ISB. The packets must be forwarded to the external network, or Internet. The local
network must be configured to use the ISB as the Default Router or Default Gateway.
Local Router
The local router is the router installed on the same network segment as the ISB. This
router requires that the Default Route be the ISB's IP address. Typically, routers have a
special entry for the Default Route. It should be configured as follows:
Destination
IP Address
The network address of the remote network segment.
For standard class "C" networks, the network address is the first 3 fields of the
Destination IP Address
. The 4
th
(last) field can be left at 0.
Subnet Mask
The Subnet Mask used on the remote network segment. For class "C" networks, the
standard Subnet Mask is 255.255.255.0
Gateway
IP Address
The IP Address of the Router on the network segment to which this device is
attached "NOT the router on the remote network segment"
Interface
Select the appropriate interface Internal (LAN) or External (WAN) from the drop-
down list.
Metric
The number of routers that must be traveled to reach the remote LAN segment. The
default value is 1.
Nexland ISB SOHO: Interface Screens
27
Destination IP
Address
Normally 0.0.0.0 but check your router documentation.
Subnet Mask
Normally 0.0.0.0 but check your router documentation.
Gateway IP Address
The IP Address of the ISB.
Metric 1
Other Routers on the Local LAN
Other routers on the local network must use the ISB's Local Router as the Default
Route. The entries will be the same as the ISB's local router, with the exception of the
Gateway IP Address.
For a router with a direct connection to the ISB's local Router, the Gateway IP Address
is the address of the ISB's local router.
For routers that must forward packets to another router before reaching the ISB's local
router, the Gateway IP Address is the address of the intermediate router.
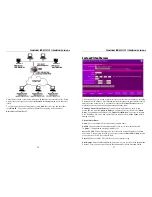
Routing Example
For the LAN shown above, with 2 routers and 3 LAN segments, the required entries
would be as follows: