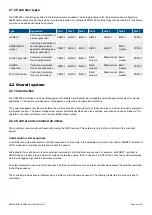
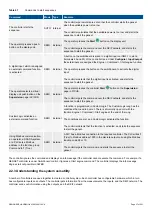
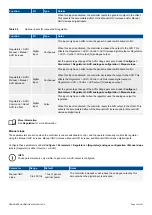
2.1.2 Controller types
The PPM 300 controller types listed in the table below are available. The hardware listed is for the recommended configuration.
Additional modules may be ordered and mounted as required. A customised PPM 300 controller may also be ordered. For example,
you may need additional inputs and outputs.
Type
Application
Slot 1
Slot 2
Slot 3
Slot 4
Slot 5
Slot 6
Slot 7
GENSET
Control and protection of
a diesel generator
PSM3.1 ACM3.1 IOM3.1 EIM3.1
GAM3.1
IOM3.1
PCM3.1
EMERGENCY
genset
Control and protection of
an emergency diesel
generator (including as a
harbour generator)
PSM3.1 ACM3.1 IOM3.1 EIM3.1
GAM3.1
Blind
module
PCM3.1
SHAFT generator
Control and protection
for a shaft generator
PSM3.1 ACM3.1 IOM3.1
Blind
module
Blind module
Blind
module
PCM3.1
SHORE
connection
Control and protection
for a shore connection
PSM3.1 ACM3.1 IOM3.1
Blind
module
Blind module
Blind
module
PCM3.1
BUS TIE breaker
Control and protection
for a bus tie breaker
PSM3.1 ACM3.1 IOM3.1
Blind
module
Blind module
Blind
module
PCM3.1
2.2 Overall system
2.2.1 Introduction
The PPM 300 Protection and Power Management controllers work together as a standard power management system for marine
applications. The system provides power management, protection and supervision functions.
The power management system calculates the control set points, although some of these can also come from third party equipment
(external set points). The power management system automatically starts and stops engines, and closes and opens breakers. The
operator, or another external source, can also initiate these actions.
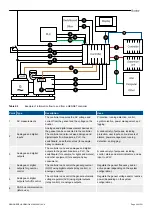
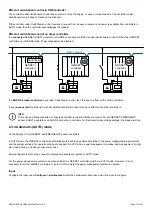
2.2.2 Control and command structure
The controllers communicate with each other using the DEIF network. This network is only for the controllers in the controller
system.
Commands to start sequences
A controller can automatically start controller sequences. For example, if the available power is too low, then a GENSET controller in
AUTO mode can automatically start and connect the genset.
Alternatively, the controller can receive external commands to start controller sequences. For example, a GENSET controller in
SEMI mode can respond to an external command to start the engine. If the controller is in AUTO mode, then the controller displays
an info message and ignores the external command.
An external command can only start a sequence if all the conditions are met, and the controller mode allows the external command
to start the sequence.
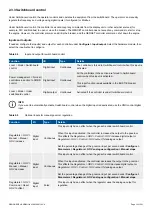
The controller provides several different ways in which to start the same sequence. The following table lists the various types of
commands.
DESIGNER'S HANDBOOK 4189340911K UK
Page 26 of 521