184
Supplementary information
Type 8792, 8793 REV.2
b) The pressure values, known at the input and output of the entire equipment (p
1
and p
2
), at which the
desired maximum flow rate Q
max
shall be reached:
1
st
step: Calculate the flow coefficient of the entire equipment k
Vtotal
according to equation (1).
2
nd
step: Determine the flow rate through the equipment without the continuous valve
(e.g. by “bypassing” the line at the installation location of the continuous valve).
3
rd
step: Calculate the flow coefficient of the equipment without the continuous valve
(k
Va
) according to equation (1).
4
th
step: Calculate the required k
VS
-value of the continuous valve according to equation (2):
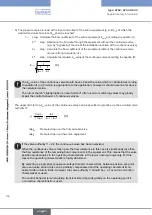
(2)
²
k
1
²
k
1
1
k
a
V
Vges
s
v
−
=
The k
VS
-value of the continuous valve should have at least the value which is calculated according
to equation (1) or (2) which is appropriate to the application, however it should never be far above
the calculated value.
The rule of thumb “slightly higher is never harmful” often used for switching valves may greatly
impair the control behavior of continuous valves.
The upper limit for the k
VS
-value of the continuous valve can be specified in practice via the so-called valve
authority Ψ:
(3)
²
k
²
k
²
k
p
p
S
V
a
V
a
V
0
0
V
+
=
∆
∆
=
ψ
)
(
)
(
(∆p)
V0
Pressure drop over the fully opened valve
(∆p)
0
Pressure drop over the entire equipment
If the valve authority
Ψ
< 0.3 the continuous valve has been oversized.
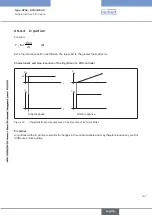
When the continuous valve is fully open, the flow resistance in this case is significantly less than
the flow resistance of the remaining fluid components in the equipment. This means that the valve
position predominates in the operating characteristic in the lower opening range only. For this
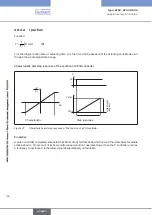
reason the operating characteristic is highly deformed.
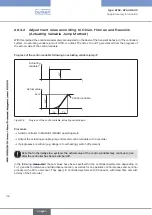
By selecting a progressive (equal percentage) transfer characteristic between position set-point
value and valve stroke, this can be partially compensated and the operating characteristic lin-
earized within certain limits. However, the valve authority
Ψ
should be > 0.1 even if a correction
characteristic is used.
The control behavior (control quality, transient time) depends greatly on the operating point if
a correction characteristic is used.
english