DL06 Micro PLC User Manual, 3rd Edition, Rev. E
5-328
Chapter 5: Standard RLL Instructions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
A
B
C
D
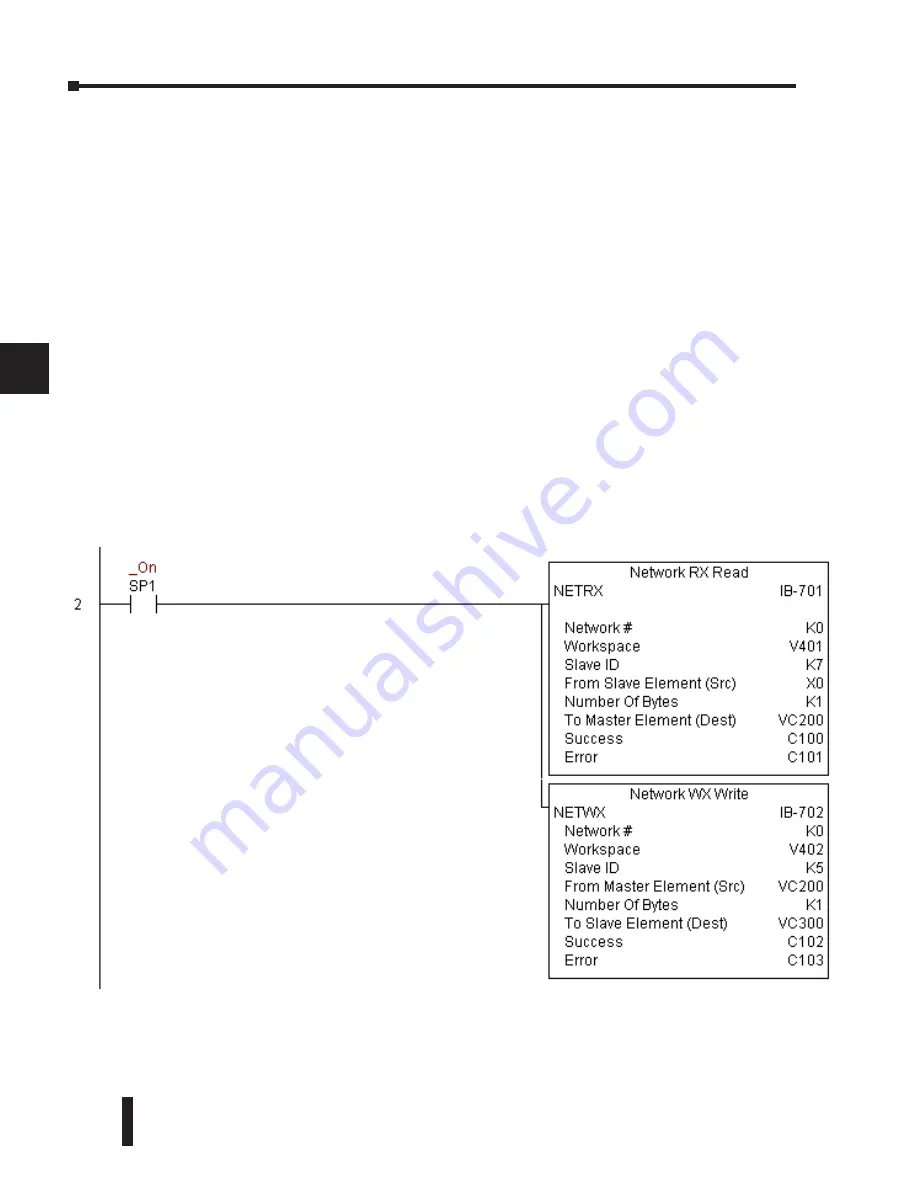
NETRX Example (cont’d)
Rung 2: Using Network# K0, read X0-X7 from Slave K7 and write them to slave K5 as fast as
possible. Store them in this local PLC in C200-C207, and write them to C300-C307 in slave
K5.
Both the NETRX and NETWX work with the Network Config IBox to simplify all networking
by handling all of the interlocks and proper resource sharing. They also provide very simplified
error reporting. You no longer need to worry about any SP “busy bits” or “error bits”, or what
port number or slot number a module is in, or have any counters or shift registers or any other
interlocks for resource management.
In this example, SP1 (always ON) is driving both the NETRX and NETWX IBoxes in the
same rung. On the scan that the Network Read completes, the Network Write will start that
same scan. As soon as the Network Write completes, any pending operations below it in the
program would get a turn. If there are no pending NETRX or NETWX IBoxes below this
IBox, then the very next scan the NETRX would start its request again.
Using the NETRX and NETWX for all of your serial port, DCM, or original ECOM network
reads and writes is the fastest the PLC can do networking. For ECOM100 modules, use the
ECOM100 and ECRX/ECWX IBoxes.
















































