55
CHAPTER2 PROFIBUS Unit
2-10
Robot language
The robot language expanded by using in the PROFIBUS unit.
2-10-1
MOVF
Function:
Moves until the specified DI or SI No. is input.
Format:
MOVF <point no.> <DI or SI No.> <input status>
Example:
MOVF 1,2,1
This command moves the robot towards P1, ends movement when D12
turns ON, and proceeds to the next step.
Explanation:
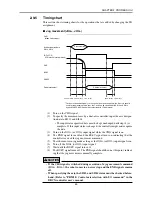
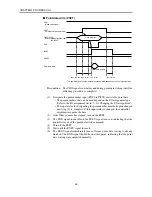
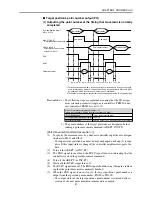
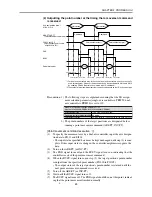
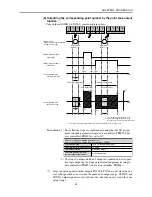
MOVF is used when searching for the target position with sensors, etc.
The robot starts movement when all axes enter the positioning-complete
pulse range, and stops when the SI and DI conditions are met. Even if the
SI or DI conditions are not met, the command ends at the stage the robot
reaches the specified point, and proceeds to the next step.
(1) Point numbers
Point numbers are identifying numbers assigned to 1,000 points in a
range from 0 to 999. These point numbers are used to create point
data in point mode. As a special usage method, when a character called
‘P’ is input here, a point variable defined by the P character is set in
the point No.
(2) DI or SI numbers
Specify one from among serial general-purpose inputs 200 - 231 (32
points) or general-purpose inputs 0 - 15 (16 points)*.
(3) Input status
Here, “1” means ON, and “0” means OFF.
Other:
• The speed during execution of the MOVF statement can be set with
the MOVF speed parameter. This has no effect on speed in OPRT
mode.
* 0 to 7 (8 points) for the SRCP/SRCD series controllers