Reference Manual
Reference
126
File Mode
The File mode provides tools for transferring data (such as Voice and
Performance) between this instrument and an external USB storage device
connected to the USB TO DEVICE terminal.
Terminology in the File mode
It is necessary to understand various terms for using the File mode. This section explains terminology specific to the File
mode.
File
Just as with a computer, various data types such as Voice and Performance created on this instrument can be treated
as a file and saved to an external USB storage device. Each file features a file name and file extension described below.
File Name
Just as with a computer, you can assign the name to the file in the File mode. The file name can contain up to 20
alphabetical characters on the display of this instrument. Files having the same name cannot be saved in the same
directory.
Extension
The three letters following the file name (after the period) such as “.mid” and “.wav” are referred to as a file “extension.”
The extension indicates the type of file and cannot be changed by the panel operation of this instrument. The File mode
of this instrument supports ten different extension types, according to the particular data.
File size
This refers to the memory amount of the file. The file size is determined by the amount of data saved to the file.
Generally, the size of an audio file including the Waveforms is much larger than the size of a MIDI file. File sizes are
indicated in conventional computer terms by B (byte), KB (kilobyte), MB (megabyte) and GB (gigabyte). 1KB is
equivalent to 1024 bytes, 1MB is equivalent to 1024KB, and 1GB is equivalent to 1024MB.
Storage
Refers to a memory storage unit (such as a hard disk) to which the file is saved. This instrument can handle and mount
various types of USB storage devices connected to the USB TO DEVICE terminal.
Directory (Dir)
This is an organizational feature on a data storage device (such as hard disk), allowing you to group data files together
according to type or application. The “directory” is equivalent to the computer term “folder.” The File mode allows you to
assign a name to a directory like a file. Please note that the directory name does not contain an extension.
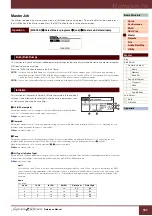
Hierarchical Structure (Tree Structure)
If you’ve saved a large number of files to memory or hard disk, you’ll want to organize those files into proper folders.
Also, if you have a large number of files and folders, you’ll want to organize those folders into a hierarchical structure,
where multiple folders are grouped into relevant ‘parent’ folders, and so on. The very top location for all your folders
(which is called up when you first open the memory location or hard disk) is called the “root directory.”
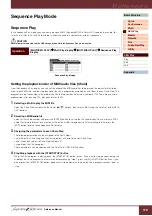
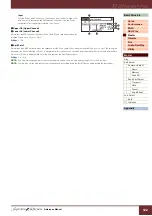
Operation
[UTILITY]
File Select display
Select “Save” or “Load”
[ENTER]