3-3 Aggregation
The Aggregation is used to configure the settings of Link Aggregation. You can bundle more
than one port with the same speed, full duplex and the same MAC to be a single logical port,
thus the logical port aggregates the bandwidth of these ports. This means you can apply your
current Ethernet equipment’s to build the bandwidth aggregation. For example, if there are
three Fast Ethernet ports aggregated in a logical port, then this logical port has bandwidth
three times as high as a single Fast Ethernet port has.
3-3.1 Static Trunk
The Aggregation Configuration is used to configure the settings of Link Aggregation. You can
bundle more than one port with the same speed, full duplex and the same MAC to be a single
logical port, thus the logical port aggregates the bandwidth of these ports. This means you
can apply your current Ethernet equipment to build the bandwidth aggregation.
3-3.1.1 Static Trunk
Ports using Static Trunk as their trunk method can choose their unique Static GroupID to form
a logic “trunked port”. The benefit of using Static Trunk method is that a port can immediately
become a member of a trunk group without any handshaking with its peer port. This is also a
disadvantage because the peer ports of your static trunk group may not know that they should
be aggregate together to form a “logic trunked port”. Using Static Trunk on both end of a link
is strongly recommended. Please also note that low speed links will stay in “not ready” state
when using static trunk to aggregate with high speed links.
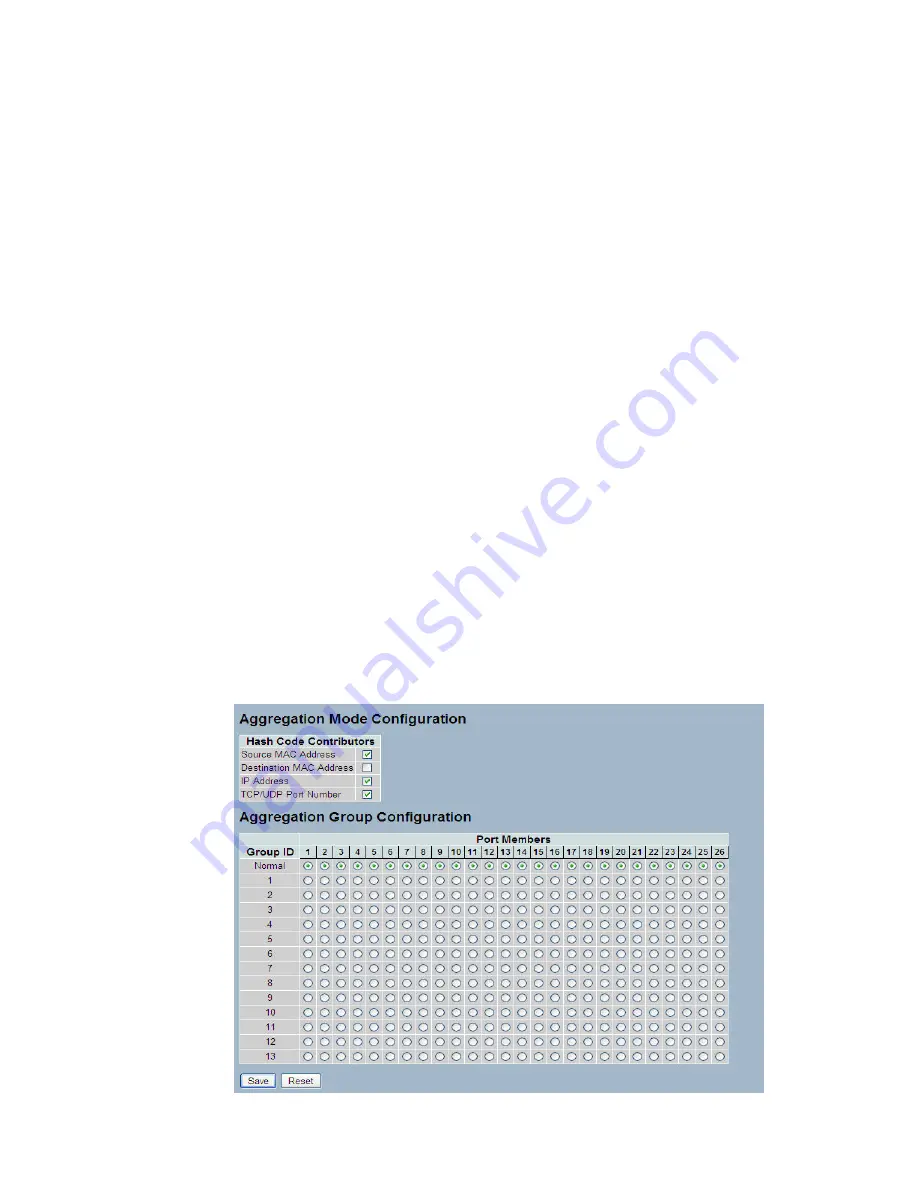
Web Interface
To configure the Trunk Aggregation Hash mode and Aggregation Group in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, Static Trunk, and then Aggregation Mode Configuration.
2. Evoke to enable or disable the aggregation mode function.
Evoke Aggregation Group ID and Port members
3. Click the save to save the setting
4. If you want to cancel the setting then you need to click the reset button. It
will revert to previous saved values.
Figure 3-3.1.1: The Aggregation Mode Configuration
















































