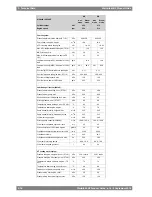
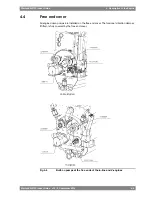
Table 5-1
Recommended maximum velocities on pump delivery side for guidance
Max velocity [m/s]
Pipe material
Piping
3
Stainless steel
LNG piping
20
Stainless steel / Carbon
steel
Fuel gas piping
1.0
Black steel
Fuel oil piping (MDF and HFO)
1.5
Black steel
Lubricating oil piping
2.5
Black steel
Fresh water piping
2.5
Galvanized steel
Sea water piping
2.5
Aluminum brass
3.0
10/90 copper-nickel-iron
4.5
70/30 copper-nickel
4.5
Rubber lined pipes
NOTE
The diameter of gas fuel piping depends only on the allowed pressure loss in the
piping, which has to be calculated project specifically.
Compressed air pipe sizing has to be calculated project specifically. The pipe sizes may be
chosen on the basis of air velocity or pressure drop. In each pipeline case it is advised to
check the pipe sizes using both methods, this to ensure that the alternative limits are not being
exceeded.
Pipeline sizing on air velocity:
For dry air, practical experience shows that reasonable
velocities are 25...30 m/s, but these should be regarded as the maximum above which noise
and erosion will take place, particularly if air is not dry. Even these velocities can be high in
terms of their effect on pressure drop. In longer supply lines, it is often necessary to restrict
velocities to 15 m/s to limit the pressure drop.
Pipeline sizing on pressure drop:
As a rule of thumb the pressure drop from the starting air
vessel to the inlet of the engine should be max. 0.1 MPa (1 bar) when the bottle pressure is 3
MPa (30 bar).
It is essential that the instrument air pressure, feeding to some critical control instrumentation,
is not allowed to fall below the nominal pressure stated in chapter "Compressed air system"
due to pressure drop in the pipeline.
5.2
Trace heating
The following pipes shall be equipped with trace heating (steam, thermal oil or electrical). It
shall be possible to shut off the trace heating.
●
All heavy fuel pipes
●
All leak fuel and filter flushing pipes carrying heavy fuel
5.3
Pressure class
The pressure class of the piping should be higher than or equal to the design pressure, which
should be higher than or equal to the highest operating (working) pressure. The highest
operating (working) pressure is equal to the setting of the safety valve in a system.
5-2
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide
5. Piping Design, Treatment and Installation
Summary of Contents for WARTSILA 50DF
Page 1: ...WÄRTSILÄ 50DF PRODUCT GUIDE ...
Page 14: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 40: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 58: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 102: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 120: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 154: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 164: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 176: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 214: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 232: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 234: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 237: ......
Page 238: ......
Page 239: ......