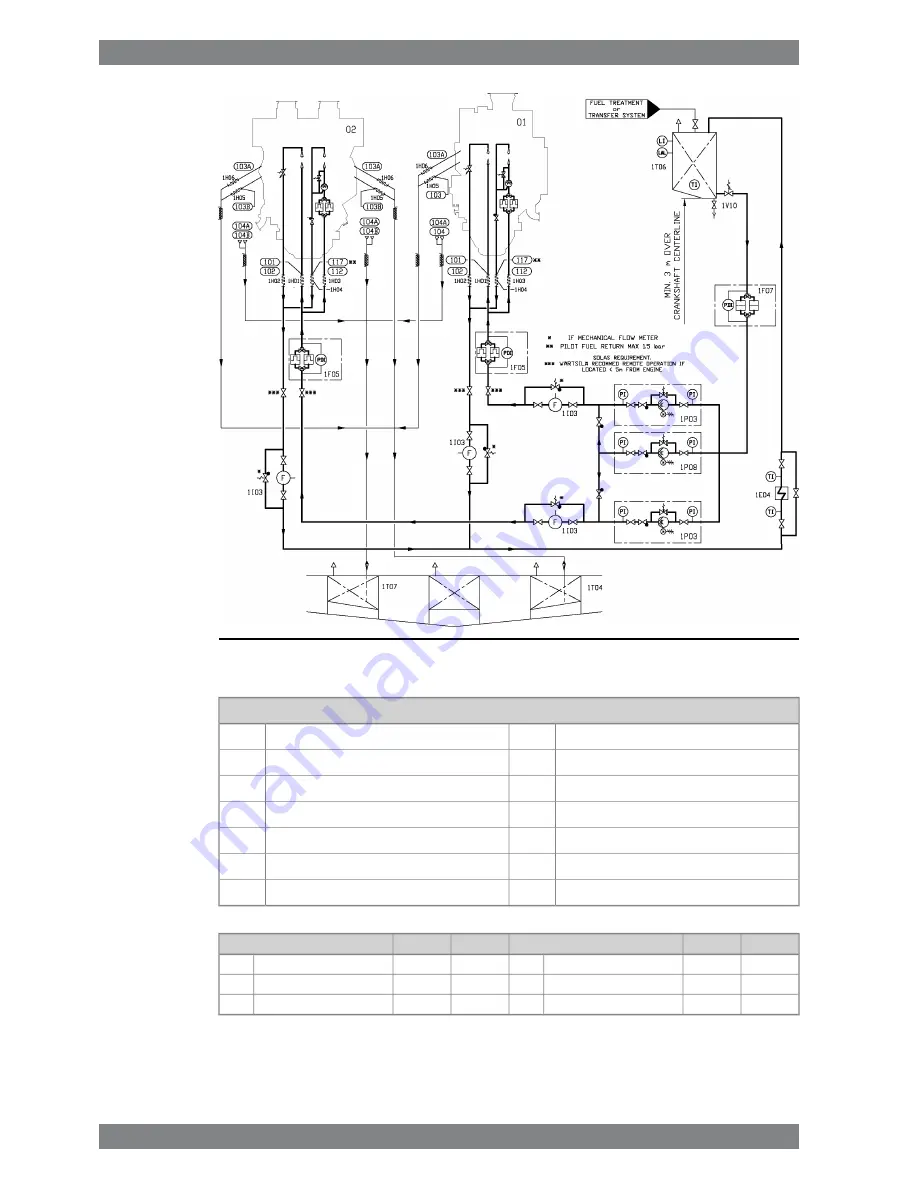
Fig 6-17
Example of fuel feed system, multiple engine with stand-by pump
(DAAF335504)
System components:
Circulation pump (MDF)
1P03
WL50DF
01
Stand-by pump (MDF)
1P08
WV50DF
02
Leak fuel tank (clean fuel)
1T04
Cooler (MDF)
1E04
Day tank (MDF)
1T06
Fine filter (MDF)
1F05
Leak fuel tank (dirty fuel)
1T07
Suction strainer (MDF)
1F07
Quick closing valve (dirty fuel)
1V10
Flexible pipe connections
1H0X
Flowmeter (MDF)
1I03
L50DF
V50DF
Pipe connections
L50DF
V50DF
Pipe connections
4*OD48
4*OD48
Leak fuel drain, dirty fuel
104
DN32
DN32
Fuel inlet
101
DN15
DN15
Pilot fuel inlet
112
DN32
DN32
Fuel outlet
102
DN15
DN15
Pilot fuel outlet
117
4*OD28
4*OD28
Leak fuel drain, clean fuel
103
6-32
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide
6. Fuel System
Summary of Contents for WARTSILA 50DF
Page 1: ...WÄRTSILÄ 50DF PRODUCT GUIDE ...
Page 14: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 40: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 58: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 102: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 120: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 154: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 164: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 176: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 214: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 232: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 234: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 237: ......
Page 238: ......
Page 239: ......
















































