4-19
W
EB
C
ONFIGURATION
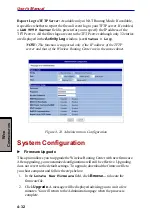
Channel ID: The radio frequency used for communication. Available channels
vary according to the regulations in your area. Select a channel out of the available
channels or use the default channel.
Advanced
Do not broadcast SSID: An AP will periodically broadcast its SSID to allow the
wireless clients to recognize its presence. However, this creates a security hole since
any wireless station with SSID set to “any” may associate with your AP. Enabling
this option is recommended in order to have your AP accept only stations whose
SSID is the same as its own.
Beacon Interval: Defines the periodic intervals at which the 802.11 Wireless LAN
Access Point sends a beacon.
RTS Threshold: Request to send threshold. It specifies the packet size beyond
which the AP invokes its RTS/CTS mechanism. Packets that exceed the specified
RTS threshold trigger the RTS/CTS mechanism.
Fragmentation Threshold: It determines whether packets will be fragmented and
at what size. On an 802.11 wireless LAN, packets that exceed the fragmentation
threshold are fragmented into smaller units suitable for the circuit size. On the other
hand, packets smaller than the wireless station’s should be used to connect to your
Access Point.
Basic Rate: Specifies the basic rate the wireless stations should use to connect to
your Access Point.
Supported Rate: Allows the AP to automatically adjust the transfer speed to the
rates you specified.
Wireless LAN Security
The Wireless Routing Center provides three types of wireless communication
security.
◆
IEEE802.1x
◆
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
◆
Access Control
The combination of these three features provides a high level of security for
Wireless LAN transmissions.
For details of IEEE802.1x functions refer to Appendix B,
Wireless LAN Security