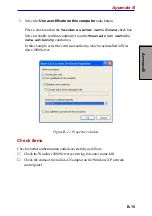
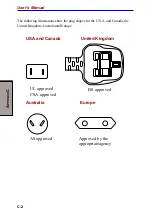
G
LOSSARY
Glossary-1
Glossary
The terms in this glossary cover the topics discussed in this manual.
10Base-T/100Base-TX: Two standards
for Ethernet data transmission speeds.
10Base-T transmits at 10Mbps and
100Base-TX transmits at 100Mbps.
A
access point name: The access point
name is used to identify a device access
point in a wireless LAN environment.
ADSL: Asymmetric Digital Subscriber
Line is a modem technology that en-
ables high-speed data communications
over existing phone lines. A splitter
enables simultaneous transmission of
voice/fax and digital data.
B
bridge: A bridge connects LANs. They
also improve efficiency of transmission
within a LAN. A basic bridge has ports
connected to two (or more) otherwise
separate LANs. Packets received on one
port may be retransmitted on another
port. A bridge will not start re-transmis-
sion until it has received the complete
packet. Therefore, stations on either side
of a bridge may be transmitting simulta-
neously without causing collisions.
C
channel: The channel is the radio
frequency used to communicate on a
wireless LAN. Wireless LANs use the
frequency band of 2.4 GHz divided into
two or more subchannels. Usable chan-
nels are restricted by the regulations in
each country. Channels 1 to 11 are
usable in the United States, for example.
D
default gateway: A gateway is an inter-
face between networks. The default
gateway is the one that is used general-
ly or when a specific gateway is not
designated.
DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol automatically sets TCP/IP
network information, such as an IP
address in each computer accessing the
Internet.
DNS: Domain Name System is an Inter-
net protocol for mapping host names,
domain names and aliases to IP ad-
dresses.
DNS relay: When a DNS client sends a
request to a DNS server, it does not go
directly to a server, instead it is routed
through a DNS relay. The DNS server's
reply is also routed through the DNS
relay, which sends it to the DNS client.