92/166
Siemens Building Technologies
Basic Documentation RVA47.320
CE1P2379E
HVAC Products
Description of the heating engineer settings
15.07.2002
In the case of tightly sized boilers and mixing heating circuits, the setpoint may
not be reached if the heating load is great, since too much heat is required for
space heating.
3
Shifting / absolute priority
If the capacity of the heat source is no longer sufficient, the mixing heating
circuits will be restricted until d.h.w. heating is terminated. The pump heating
circuits will be locked until d,h.w. is heated up.
Frost protection for the plant is fully active only in the case of setting 2. With setting 0 or
1, it will be partly or fully restricted. If the boiler is correctly sized, frost protection for the
plant is also ensured when using setting 1. In the case of plants where there is a
considerable risk of frost (e.g. plants with outdoor heating), setting 0 should not be
used.
4.43.1
Shifting priority
The purpose of the function "Shifting priority" is to achieve optimum d.h.w. heating. This
means that during d.h.w. heating, the actual boiler temperature should be as close as
possible to the boiler temperature setpoint without shutting down the burner. To
achieve this, it may be necessary to restrict the heating circuits by means of a locking
signal. The signal is generated by a temperature-time integral.
Depending on the consumer, the locking signal will lead to switching on / off or a
setpoint reduction.
Cycling or deactivation of the pumps will reduce the amount of heat drawn from the
heat source. This will considerably shorten the time required for heating up the d.h.w.
•
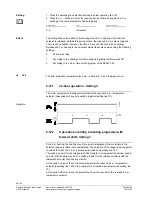
Heating circuit pump:
Status Effect
Locking signal < 20 %
Normal pump operation
Locking signal > 20 %
Heating circuit pump cycles
Locking signal > 93 %
Heating circuit pump OFF
•
D.h.w. pump or boiler pump:
No
effect
Through the generation of the temperature-time integral it is not only the period of time
that is considered, but also the extent of the undershoot. This means that when the
crossing is significant, the pumps will be deactivated earlier.
The consumption of heat is considerably reduced through the reduction of the flow
temperature setpoints. This reduces considerably the heating up time for d.h.w., with a
minimum impact on the heating circuits.
•
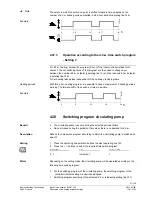
Mixing valve:
Status Effect
Locking signal > 0 %
Flow temperature setpoints will be lowered.
The extent of lowering is dependent on the magnitude and the period of
time of the undershoot.
Locking signal reduced to
0 %
Setpoints according to the normal control condition
Through the generation of the temperature-time integral it is not only the period of time
that is considered, but also the extent of the undershoot. This means that when the
undershoot is significant, the setpoint reduction will be greater.
Frost protection for the
plant
Impact on 2-position
loads
Switching point
Impact on modulating
loads
setpoint reduction