SP LINK | Using SP LINK
66
|
Doc #OI0003 Part #004122 Rev 04 2010
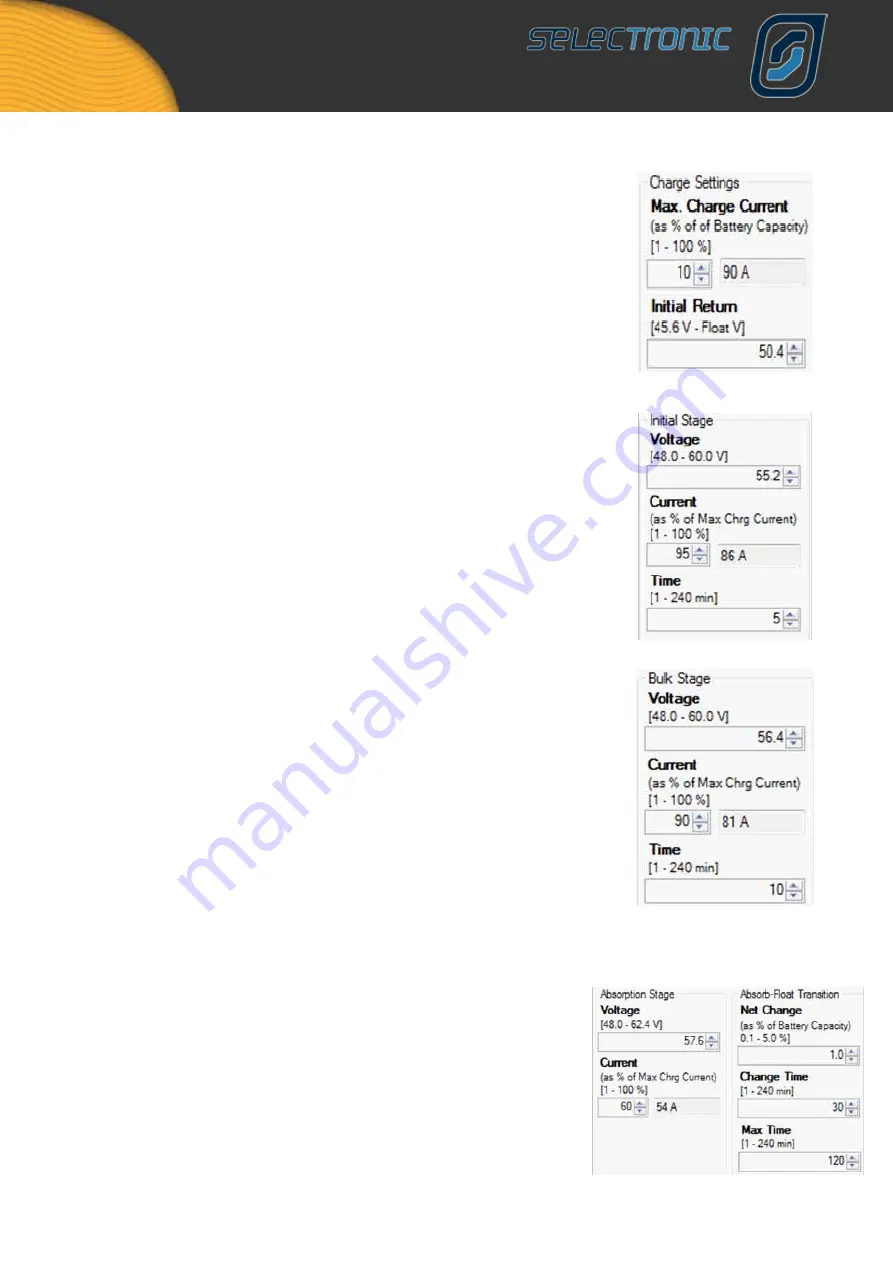
MAx. CHARGE CURRENT
is the maximum charge current that the inverter will send
to the batteries under any circumstances (including all external charge currents)
at any charge stage. This is expressed as a percentage of your battery capacity.
For example if your battery pack is rated at 900 amp hours capacity and your
battery manufacturer suggests a maximum charge current of 10% of capacity (quite
common) then you would set this figure at 10% and the maximum charge current limit
would be set at 90 amps.
This means that if there is 40A of solar charge current when the inverter is charging,
then the inverter will only put 50A of charge into the battery.
Initial Return is the voltage level at which the charge cycle will return to the beginning,
or Initial, stage of the charge process. The 10 second average battery voltage must
remain at or below this level for 2 minutes to switch to Initial. This response time
ensures that short term loads do not prematururly cause the charger to reset to Initial.
The maximum voltage settable is the lowest float voltage (either Float or Long term
Float) minus 5%.
The purpose of the
INITIAL STAGE
of the charging process is to raise the battery
voltage quickly with a large charge current. In this section you set the voltage you
wish the batteries to reach, the current you wish to charge at and the length of time
the batteries will stay at that voltage until the inverter moves to the next stage of the
charge cycle.
The current is expressed as a % of the maximum charge current. Using our previous
example if the maximum charge current was 90amps and you wish to charge, in this
stage, at ~85 amps you would insert 95 in this area. ie 95% of 90 amps = 85.5amps
BULK STAGE
is the part of the charge cycle where the majority of the charging takes
place. This is normally set at a higher voltage than the initial stage but at a lower
charge current. The time section determines, once the Bulk voltage is reached, how
long the batteries stay at this level until the inverter starts the next stage of the charge
process. Once again using our example if you wanted this stage to charge at ~80
amps you would insert 90 as the setting because 90% of 90 amps is 81 amps. The
time that the charge stage would remain at this voltage would normally be longer
than in the initial stage.
THE ABSORPTION STAGE
is the part of the charge process that allows the batteries
to maximise the effect of the previous charge stages. This stage is normally set to
a higher Voltage than the two previous stages but a lower charge Current. The Max
Time it would remain in this stage is longer again than the previous stages.
This section has a further level of control in that it will also end this stage if the charge
current does not change below the figure set at Net Change for a period of time
(Change Time).
For example if you have set your absorption voltage to 57.6 volts, the current to 60%
(54 amps) and the Max Time to 120 minutes, then the battery will be charged at 54A
until the battery voltage reaches 57.6 volts. At this point the battery charging process
will change from Absorption into Float based on the rate of change in charge current
over a period of time.. If for example you have a battery bank of 900Ah, Net change
is set to 1% and change time set to 30 minutes, then transition to Float will occur
when net battery charge current has not changed by more than 9A in 30 minutes.
If transition to Float has not occurred before Max Time expires then absorption stage
will be terminated anyway as this may suggest a faulty battery cell.
















































