PA-02
PID feedback
source
Default
:
0
0: PA-01 setting
0: Ai1 1: Ai2
2: AI3/panel potentiometer
3: AI1-AI2 4
: Pulse setting (X6)
5: Communication given
6: AI1+AI2 7:MAX(|AI1|, |Ai2|)
8:MIN(|AI1|, |AI2|)
The feedback amount of the process PID is also a relative value, and the
setting range is 0.0% to 100.0%.
This parameter is used to select the feedback signal channel of the
process PID.
PA-03
PID action direction
Default
:
0
0: Forward action
1: Reverse action
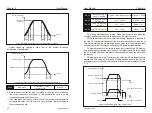
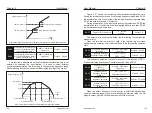
Forward action: When the PID feedback signal is less than the given
amount, the inverter output frequency rises. Such as winding tension control
occasions.
This function is affected by the reverse direction of the multi-function
terminal PID (function 35), so you need to pay attention to it during use.
Reverse action: When the feedback signal of the PID is less than the given
amount, the output frequency of the inverter decreases. Such as unwinding
tension control occasions.
PA-04
PID given feedback range
Default
:
1000
0
~
65535
PID given feedback range is a dimensionless unit for the PID given display
U0-15 and the PID feedback display U0-16. The relative value of the given
feedback of the PID is 100.0%, corresponding to the given feedback range
PA-04. For example, if PA-40 is set to 2000, when the PID is given 100.0%,
the PID given display U0-15 is 2000
PA-05
Proportional gain Kp1
0.0
~
100.0
Default
:
20
PA-06
Integration time Ti1
0.01s
~
10.00s
Default
:
1s
PA-07
Derivative time Td1
Default
:
2.00s
0.000s 10.000s
User Manual
138
User Manual
139
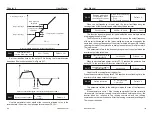
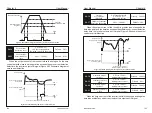
Determine the adjustment strength of the entire PID regulator, the larger
the Kp1, the greater the adjustment intensity. The parameter 100.0 indicates
that when the deviation between the PID feedback amount and the given
amount is 100.0%, the adjustment range of the PID regulator to the output
frequency command is the Maximum frequency.
Integration time Ti1: Determines the strength of the PID regulator integral
adjustment. The shorter the integration time, the greater the adjustment
intensity. The integration time means that when the deviation between the
PID feedback amount and the given amount is 100.0%, the integral regulator
continuously adjusts through the time, and the adjustment amount reaches
the Maximum frequency.
Proportional gain Kp1:
Derivative time Td1: Determines the strength of the PID regulator's
adjustment to the rate of change of the deviation. The longer the
differentiation time, the greater the adjustment intensity. The derivative time
means that when the feedback amount changes by 100.0% during this time,
the adjustment amount of the differential regulator is the Maximum
frequency.
The set target amount of the process PID is a relative value, and the
setting range is 0.0% to 100.0%. The feedback amount of the same PID is
also the relative amount, and the role of the PID is to make the two relative
quantities the same
This parameter is used to select the target channel for the process PID.
PA-08
PID reverse cutoff frequency
Default : 2.00Hz
0.00
~
Maximum
frequency
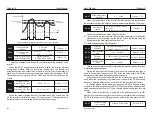
In some cases, only when the PID output frequency is negative (the
inverter reverse rotation), it is possible for the PID to control the given amount
and the feedback amount to the same state, but the excessive reverse
frequency is not allowed for some occasions. PA-08 is used to determine the
upper limit of the inversion frequency.
PA-09
PID deviation limit
Default 0.0%
0.0%
~
100.0%
P When the deviation between the PID given amount and the feedback
amount is smaller than PA-09, the PID stops the adjustment action. In this
way, the output frequency is stable when the deviation from the feedback is
small, which is effective for some closed-loop control applications.
PA-10
PID differential limiting
Default 0.10%
0.00%
~
100.00%
In the PID regulator, the function of the differential is relatively sensitive,
and it is easy to cause the system to oscillate. For this reason, the role of the
PID differential is generally limited to a small range, and the PA-10 is used to
set the range of the PID differential output.
Chapter 6
Chapter 6