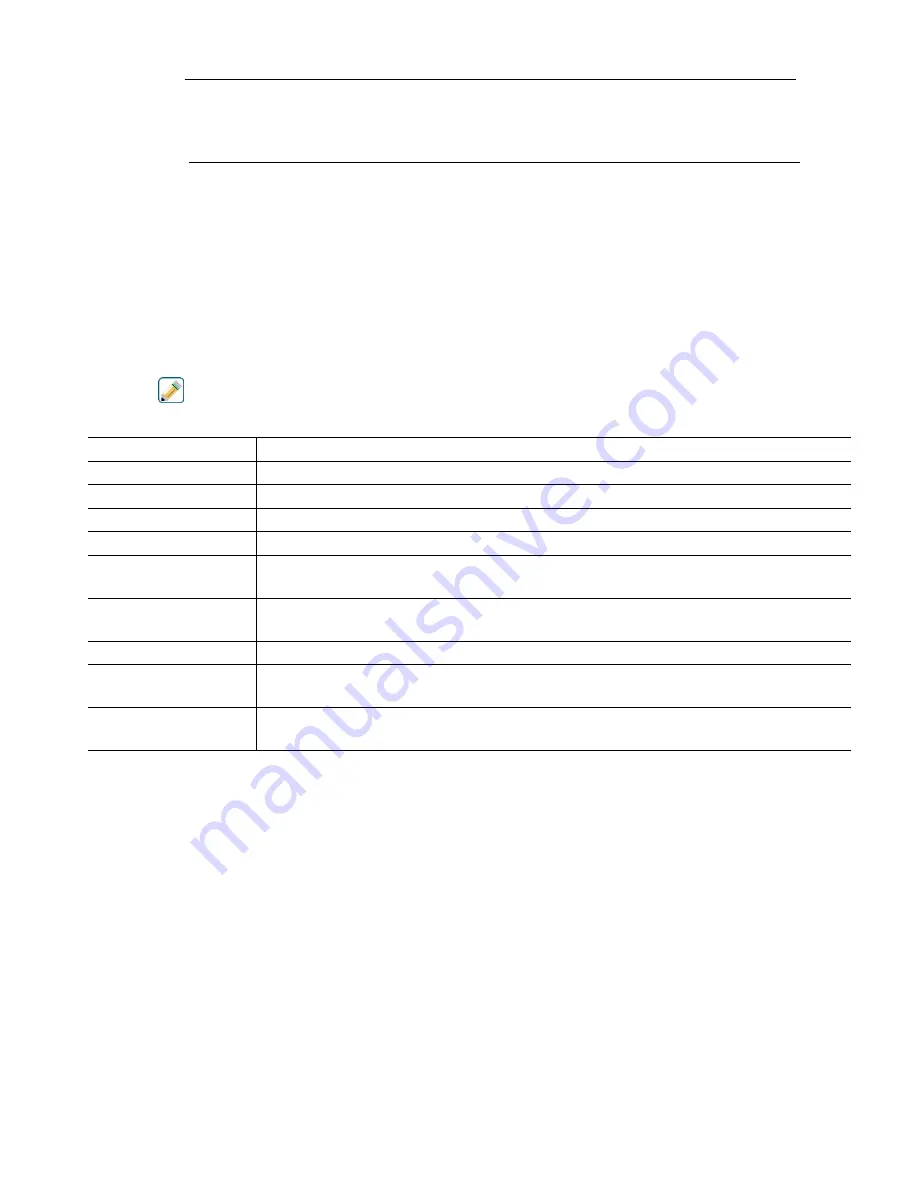
101
% output = Target PPM
x Water Flow Rate (liter/min or gal/min)
Cycles x Pump Rating (liter or gal/hr) x Pump Setting (%) x Specific Gravity x 166.67
% output = Target PPM
x Water Flow Rate (m3⁄min)
Cycles x Pump Rating (liter/hr) x Pump Setting (%) x Specific Gravity x 0.16667
Control Operation
If the output is continuously on for longer than the Output Time Limit, then output will deactivate.
Output Details
The details for this type of output include the output %, HOA mode or Interlock status, alarms related to this out-
put, current cycle on time, total accumulated on-time, cycles of concentration, mA output, and the current control
mode setting.
Settings
Touch the Edit icon to view or change the settings related to the output.
Target
Enter the desired PPM set point for the product.
Pump Capacity
Enter the maximum flow rate for the metering pump.
Pump Setting
Enter the stroke length setting for the metering pump, in percent.
Specific Gravity
Enter the specific gravity of the product to be added.
Hand Output
Enter the output % desired when the output is in Hand mode.
Off Mode Output
Enter the output mA value desired when the output is in Off mode, or being Interlocked, or
during a calibration of the sensor being used as an input. The acceptable range is 0 to 21 mA.
Error Output
Enter the output mA desired when the sensor is not giving the controller a valid signal.
The acceptable range is 0 to 21 mA.
Flow Input
Select the flow meter to be used as an input for this control relay.
Cycles Input
Select the virtual input that is programmed as a Ratio calculation of the system
conductivity/makeup conductivity, or select None.
Low Cycles Limit
Enter the lower limit for cycles of concentration, if used. The calculated on-time is limited
to a maximum value if the cycles of concentration gets too low.
5.3.31
Analog or Control Outputs, PID Control Mode
ONLY AVAILABLE IF CONTROLLER INCLUDES ANALOG OUTPUT HARDWARE & HVAC MODE IS DISABLED
The PID algorithm controls an analog (4-20 mA) output using standard Proportional-Integral-Derivative control
logic. The algorithm provides feedback control based on an error value continuously calculated as the difference
between a measured process variable and a desired set point. Tuning settings specify the response for proportional
(the size of the error), integral (the time that the error has been present), and derivative (the rate of change for the
error) parameters. With proper tuning, the PID control algorithm can hold the process value close the set point
while minimizing overshoot and undershoot.
Normalized Error
The error value versus set point that is calculated by the controller is normalized and represented as percent of full
scale. As a result, tuning parameters entered by the user are not dependent upon the scale of the process variable
and the PID response with similar settings will be more consistent even when using different types of sensor
inputs.
The scale used to normalize the error is dependent upon the type of sensor selected. By default, the full nominal
range of the sensor is used. This range is editable by the user if tighter control is desired.
















































