- 40 -
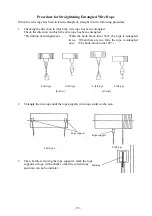
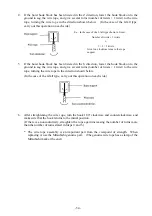
Problem
Cause Remedy
5. The 2nd-stage limit
switch operates.
(1) Incorrect connection of power supply line
(2) Wire rope wound reversely
(1) Exchange the phases R and T
of the power supply.
(3) Although the use of the no-load high-speed
function has been specified, the upper limit stop
point has not been set. Or the upper limit set
position is too high.
(2) Set the upper limit correctly.
(3) Set the upper limit to the
proper position.
6. Wire rope is cut.
(1) The rope catches on something during hoisting.
(2) Corrosion due to chemicals
(3) Use of badly worn wire rope
(1) Handle and maintain the rope
properly. Replace the
defective wire rope.
(Use the Mitsubishi genuine
wire rope.)
7. The hoist does not
start even if the
pushbutton is
pressed.
(1) Pushbutton defective, or pushbutton cable
broken
(1) Repair, replace, or cut out.
(2) Incorrect wiring of power switch, fuse, contactor,
or pushbutton, imperfect contact of trolley line,
loose screws, etc.
(2) Check, and repair. See the
expanded connection diagram.
(3) The inverter does not give 3-phase output.
(3) Check the inverter.
(4) No signal is returned from the sensor, or one of
the rotation signals (signals for 2 phases) is not
returned from the RRS board.
(4) Check and replace the RRS
board. Check the signal line
(microphone cord) for dis-
connection.
(5) The hoisting motor torque is insufficient for
overload, and the hoist stops.
(5) Reduce the load.
(6) The hoisting motor overheats due to too frequent
use, the torque drops, and the hoist stops.
(6) Use the hoist at appropriate
intervals.
8. The hoist lowers and
stops during hoisting
(1) Overload
(1) Reduce the load.
(2) Hoisting motor overheat
(2) Use the hoist at appropriate
intervals.
(3) Hoisting motor wire breakage
(3) Check, and repair.
9. The hoist stops
suddenly during
hoisting.
(1) Inverter trip due to overvoltage caused by
hoisting an overload.
(1) Reduce the load.
(2) Inverter overvoltage tripping is caused due to rise
in the resistance value that is caused by
temperature rise of the discharging resistor due to
too frequent use.
(2) Use the hoist at appropriate
intervals.
(3) Disconnection of discharging resistor
(3) Check, and repair.
10. Power is applied to
the traversing motor,
but the motor growls
and takes a longer
time (2 sec. or more)
to start.
(1) Electric resistance is high due to wiring, switch
or trolley contact failure or loosened screws.
(Voltage drop at start)
(1) Check, and repair.
(2) Wires too thin or long
(2) Change the wiring in accord-
ance with the selection table.
(3) Supply voltage too low.
(3) Change the transformer taps.
(4) Electromagnetic brake not released.
(4) See Item 14.
(5) Defective electromagnetic brake coil.
(5) Replace the coil.
11. The hoist suddenly
stops during lifting
or lowering
operation.
(1) The 1st-stage limit switch functions.
(1) Lower the load.
(2) Inverter trip due to too low supply voltage
(2) Change the transformer taps.
(3) Hoisting brake works.
(3) See Item 14.
(4) Inverter trip due to overload or ground lifting
(4) Re-examine the lowering
method and load.
(5) Fall caused by overload is detected.
(5) Re-examine the lowering
method and load.
(6) Malfunction due to noise.
(6) Fit a noise filter to the 3-phase
power supply.
Summary of Contents for UM 10t
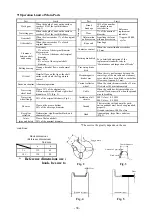
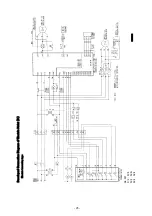
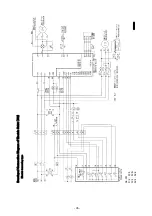
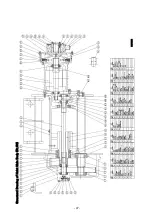
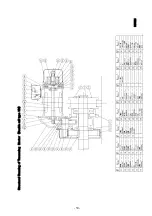
Page 51: ... 47 Structural Drawing of Hoist Main Body 5t 10t PA00531 ...
Page 52: ... 48 Structural Drawing of Electric Traversing Unit Monorail Type 10t P288922 ...
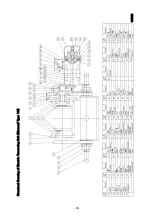
Page 53: ... 49 Structural Drawing of Electric Traversing Unit Double rail type 5t PA00483 ...
Page 54: ... 50 Structural Drawing of Traversing Mortor Double rail type 10t P276926 ...
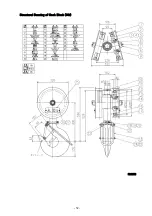
Page 55: ... 51 Structural Drawing of Hook Block 5t PG49975 ...
Page 56: ... 52 Structural Drawing of Hook Block 10t PG49976 ...