Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
55
Thermal Specifications
6.2.2.2
Clock Modulation
Clock modulation is a second method of thermal control available to the processor.
Clock modulation is performed by rapidly turning the clocks off and on at a duty cycle
that should reduce power dissipation by about 50% (typically a 30-50% duty cycle).
Clocks often will not be off for more than 32 microseconds when the TCC is active.
Cycle times are independent of processor frequency. The duty cycle for the TCC, when
activated by the Thermal Monitor, is factory configured and cannot be modified.
It is possible for software to initiate clock modulation with configurable duty cycles.
A small amount of hysteresis has been included to prevent rapid active/inactive
transitions of the TCC when the processor temperature is near its maximum operating
temperature. Once the temperature has dropped below the maximum operating
temperature, and the hysteresis timer has expired, the TCC goes inactive and clock
modulation ceases.
6.2.2.3
Immediate Transition to combined TM1 and TM2
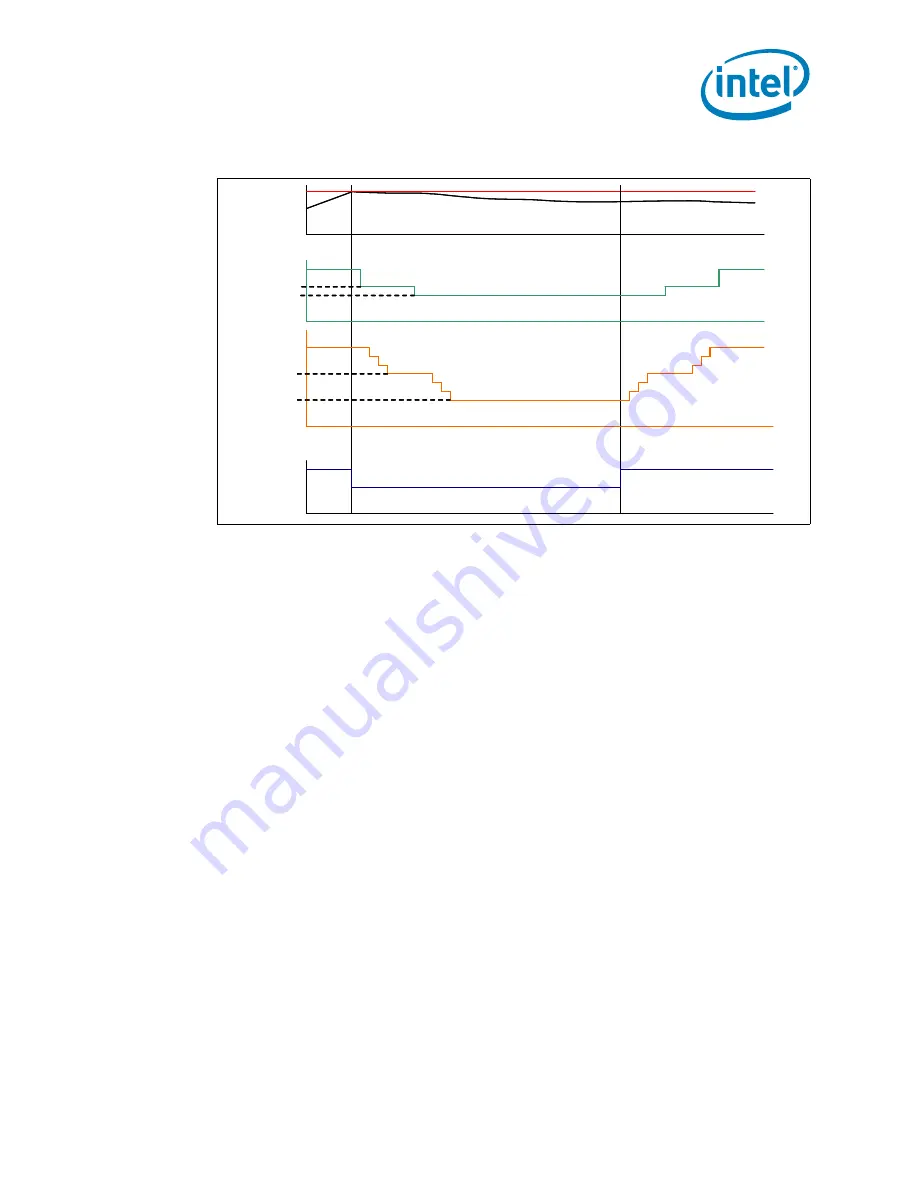
As mentioned above, when the TCC is activated the processor will sequentially step
down the ratio multipliers and VIDs in an attempt to reduce the silicon temperature. If
the temperature continues to increase and exceeds the TCC activation temperature by
approximately 5
o
C before the lowest ratio/VID combination has been reached, then
the processor will immediately transition to the combined TM1/TM2 condition. The
processor will remain in this state until the temperature has dropped below the TCC
activation point. Once below the TCC activation temperature, TM1 will be discontinued
and TM2 will be exited by stepping up to the appropriate ratio/VID state.
Figure 6-6. Frequency and Voltage Ordering
Temperature
f
MAX
f
1
f
2
VIDf
MAX
VID
Frequency
VIDf
2
VIDf
1
PROCHOT#
Temperature
f
MAX
f
1
f
2
VIDf
MAX
VID
Frequency
VIDf
2
VIDf
1
PROCHOT#
Summary of Contents for 2ND GENERATION CORE PROCESSOR FAMILY DESKTOP - THERMAL MECHANICAL S AND DESIGN GUIDELINES 01-2011
Page 12: ...Introduction 12 Thermal Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines...
Page 36: ...Independent Loading Mechanism ILM 36 Thermal Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines...
Page 62: ...PECI Interface 62 Thermal Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines...
Page 88: ...ATX Reference Thermal Solution 88 Thermal Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines...
Page 102: ...Boxed Processor Specifications 102 Thermal Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines...
Page 120: ...Mechanical Drawings 120 Thermal Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines...
Page 126: ...Socket Mechanical Drawings 126 Thermal Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines...
Page 130: ...Package Mechanical Drawings 130 Thermal Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines...
















































