3.4 Maintenance, Diagnostic Commands
C141-C010
3-115
3.4.4
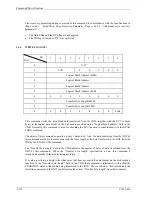
READ BUFFER (3C)
Bit
Byte
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
0
X‘3C’
1
LUN
0
Mode
2
X‘00’ (Buffer ID)
3
Buffer Offset (MSB)
4
Buffer Offset
5
Buffer Offset (LSB)
6
Transfer Byte Length (MSB)
7
Transfer Byte Length
8
Transfer Byte Length (LSB)
9
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Link
This command is used in combination with the WRITE BUFFER command to diagnose the normalcy of
the IDD’s data buffer memory and the SCSI bus.
The functions of this command and the contents of the data transferred to the INIT are specified by the
“Mode” field in the CDB and one of the transfer modes shown below can be selected.
“Mode” Bit
3 2 1 0
Transfer Mode
0
0
0
0
Data, without Address Specification
0
0
0
1
Data, with Address Specification
0
0
1
0
Data Only, with Address Specification
0
0
1
1
Buffer Descriptor
1
0
1
0
Echo buffer
1
0
1
1
Echo buffer descriptor
(1)
Mode = 0, 0, 0, 0: data, without address specification
When this mode is specified, the data stored in the IDD’s data buffer are transferred to the INIT after the
4-byte header. Zero must be specified in the “Buffer offset” field in the CDB.
Summary of Contents for 80
Page 4: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 10: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 18: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 62: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 284: ...Sense Data Error Recovery Methods This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 296: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 298: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 308: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 309: ......
Page 310: ......