OPERATING PRINCIPLES
I
1
- CLEANING CYCLE
I
1.2 - Cleaning of the Plastic Trough (35).
The plastic trough (35) will reach its maximum lower position to discharge the water from the last cycle which was
interrupted by the shutdown of the Machine. This cleaning cycle is necessary due to safety and hygiene reasons,
because we could not quantify the time that the Ice Machine is turned off, with water inside the plastic trough (35).
1.1 - Initialization
Every time the machine is energized (connected to the power grid, switched on again by the tank's thermostat
(61) or after a power surge), the cleaning cycle for the plastic trough (35) and evaporator (20) starts up. The
signaling LEDs - LD1 (maintenance), LD2 (water shortage) - for the circuit board (62) and the LED board (68),
light up for a period of 02 seconds, in order to inform the start-up of the system's operation.
2
- ICE FORMATION CYCLE
2.1 - Formation
After the cleaning cycle, the plastic trough (35) returns to the highest position, the circuit board (62) switches on
the water valve (63) to let water in the the plastic trough (35), the mobile water sensor (55) indicates to the
circuit board (62) when the water level of the plastic trough (35) touches it, and switches off the water valve (63).
With the cooling system in operation, the formation of ice around the cube makers in the evaporator begins (20),
such cubes will grow to a thickness that obstructs the passage of the plastic fins (29) which rotate continuously
.
3
- ICE DETACHMENT CYCLE
The purpose of the tank thermostat (61), whose bulb is fixed below the equipment's water draining tray, is to
switch the equipment off when it is filled with ice and turn it back on when the ice level in the tank (6) decreases.
In the EGC-50A model, the thermostat bulb is fixed in the tank. (6)
3.1 - “Quick Stop”
After 45 seconds, the circuit board (62), switches on the gear motor (60) to lower the plastic trough (35) and
discharge the residual water from the ice formation cycle. In this lowering interval, the plastic trough (35) will
perform a temporary stop, this action avoids the residual water - which is close to zero degrees - from reaching
the tank thermostat (61) and switching off the Ice Machine unnecessarily.
4
- OPERATION OF THE TANK THERMOSTAT
8
1.3 - Evaporator Cleaning (20).
With the plastic trough (35) at the lowest position, the gas solenoid valve (28) is activated for 45 seconds, cleaning
the evaporator from ice cubes.
3.2 - Ice detachment cycle.
With the plastic trough (35) positioned at the lowest point, the by-pass cycle begins. The circuit board (62)
switches on the gas solenoid valve (28), which allows the hot gas to enter directly into the evaporator (20),
detaching the ice cubes. After 45 seconds of By Pass, the circuit board (62) switches on the micro gear box (57)
for 5 seconds and checks whether the finned axis (50) is still blocked by any ice cube. If the finned axis (50) is
blocked, the by-pass time is increased by 5 more seconds, as often as needed, for up to 2 minutes. In case it is
unblocked, the circuit board (62) switches off the gas solenoid valve (28) and switches on the motor gear (60),
returning the plastic trough (35) to the highest point and restarting a new ice formation cycle.
2.2 - Growing cycle
When the ice cubes grow up to a thickness that prevents the rotation of the plastic fins (57), the micro gear
motor coupled to the finned axis (50) activates the end of cycle micro switch (59), indicating to the circuit board
(62) that the ice formation cycle is completed. In this moment, the circuit board (62), switches off the micro gear
motor (57). The system will wait for 10 seconds with the plastic trough (35) on the highest position, allowing
the residual water from the ice formation cycle to be used, increasing the volume of ice cubes and reducing the
volume of water discharged.
1.4 - The fan (24).
The fan (24) is activated through the micro switch (46). The micro switch (46) is fixated on the left panel of the
cylinder head (44), in a way that its rod is activated by the plastic trough (35). When the trough is lowered, the micro
switch (46) opens and it switches off the fan (24). This action assists the detachment of the ice cubes. When the
BYPASS is finished, the plastic trough (35) is elevated, the micro switch (46) is closed and the fan is switched on (24)
Summary of Contents for EGC 100 A / 150 A
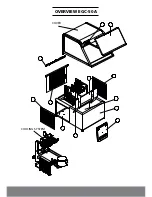
Page 12: ...OVERVIEW EGC 50A COVER COOLING SYSTEM...
Page 14: ...13 I OVERVIEW EGC 150MA I...
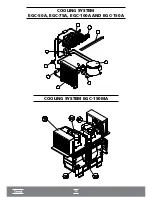
Page 15: ...14 COOLING SYSTEM EGC 50A EGC 75A EGC 100A AND EGC 150A I COOLING SYSTEM EGC 150MA I...
Page 16: ...ELECTRICAL ELECTRONIC PART...
Page 17: ...TROUGH DISPLACEMENT SYSTEM DISPLACEMENT ARM ASSEMBLY TROUGH...
Page 36: ...35...