Flue
The flue of a pellet stove is a very important component because it affects the correct working of
the stove.
The flue must be only for the stove and cannot be used for
other apparatus; you can’t make fixed or movable openings
to connect other air adduction pipes and pipes for plant-
engineering use.
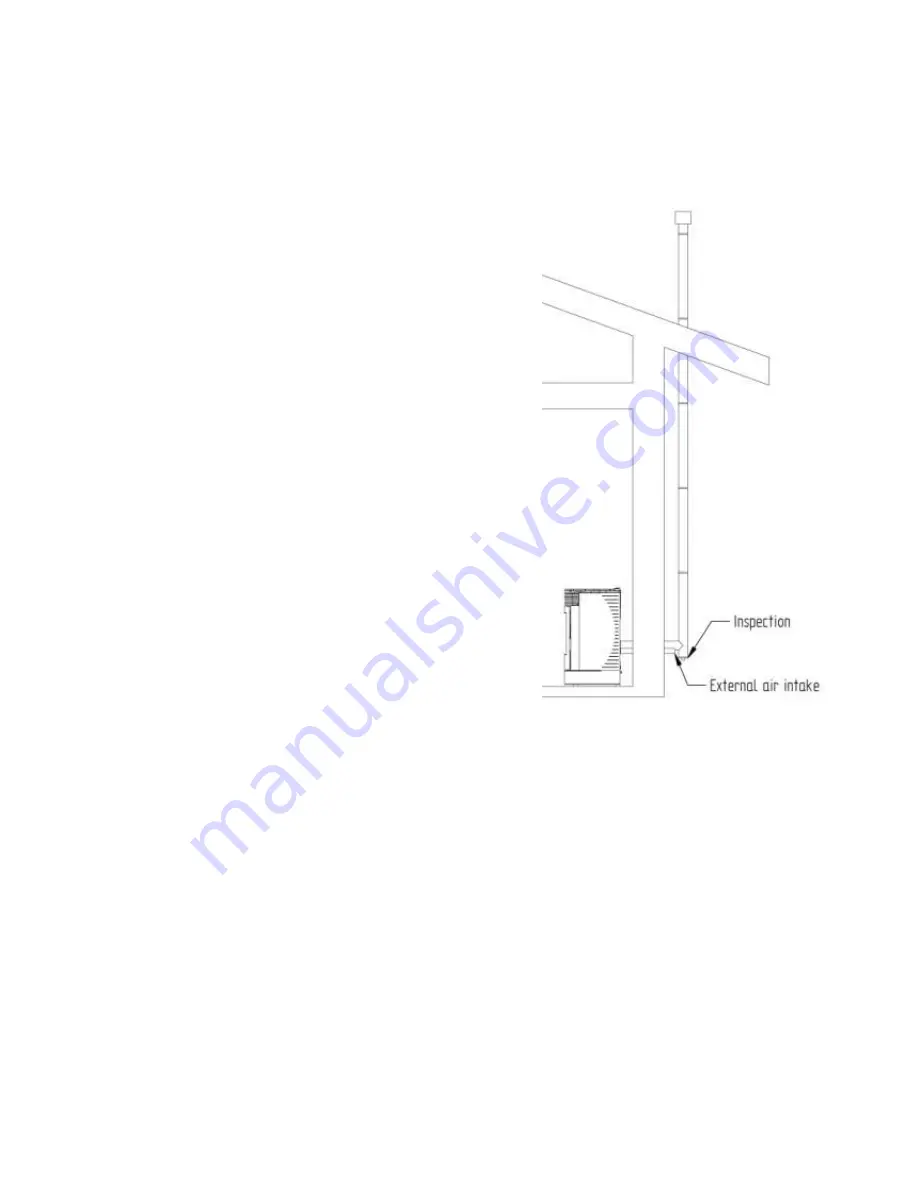
The flue must be equipped with a chamber for the
gathering of solid materials and possible condensations,
placed under the entrance of the flue outlet duct, so that
you can easily open it and inspect it from an airtight small
door.
The installer has to make sure the opening do not cross
inflammable materials, or in the absence of alternative
solutions, he has to use an insulating protection on the
pipe ( with wall junctions with a diameter of 13 cm at least,
insulating the pipe with insulating materials 1,5-5 cm thick,
with a suitable thermal conductivity), even if it passes near
inflammable materials ( minimum distance 200 mm).
As for the assembly of the pipes you must always use pipes
and junctions with hermetically sealed gaskets.
It’s important that the curvature of 90° provides for a T
junction with inspection; we advise you to use a curve of
45°.
Using nets or filters at the extremity of the flue or any extremity which could turn into a
nest is forbidden. Use only extremity in accordance with the regulation.
The horizontal segments must have a minimum inclination of 3% upward.
As for the connection of the flue, the horizontal segment must be minimum and you
mustn’t exceed 3 meters, the number of direction changes, including that owing to the use
of the T element, mustn’t be bigger than 4, never exceed 6 m of pipes, use curves of 45°
and obey the regulations
UNI 10683
, using pipes in accordance with the law.
Examples of connections with isolated and non-isolated external pipes
Connections that provide for the use of pipes not larger than 20 cm in diameter, which must have
at the base an inspection system and a draught less than 10 Pa. The internal section must be
uniform, preferably circular; the sides of the pipe must be smooth as much as possible and without
narrowings; the curves must be regular and without discontinuities; the pipes mustn’t be subjected
to deviations from the axis higher than 45°.










































