82
Maintenance
Contamination Levels
Clean fluid implies the absence of impurities such
as solid particles, water and air. Contamination
control includes proper design, installation, and
maintenance of hydraulic components.
The reservoir is designed to limit entry of
contamination during servicing and operation. A
sealed reservoir with a low pressure relief valve
reduces the introduction of contaminants while
maintaining inlet and case drain pressures below
the maximum recommended.
The purpose of the filter in a system is to clean
the oil at initial start up and to maintain acceptable
levels of particle contaminants as they are ingested
or generated during operation of the system.
Filtration is a matter of controlling the particle
sizes and their respective quantities to appropriate
levels so as to avoid degradation of the system
components and thereby assure the desired life.
Fluid contaminant profile requirements for Etnyre
hydraulic units have been determined empirically
based on measuring fluid quality in successful
application, and in laboratory tests designed to
evaluate hydraulic unit contaminant sensitivity.
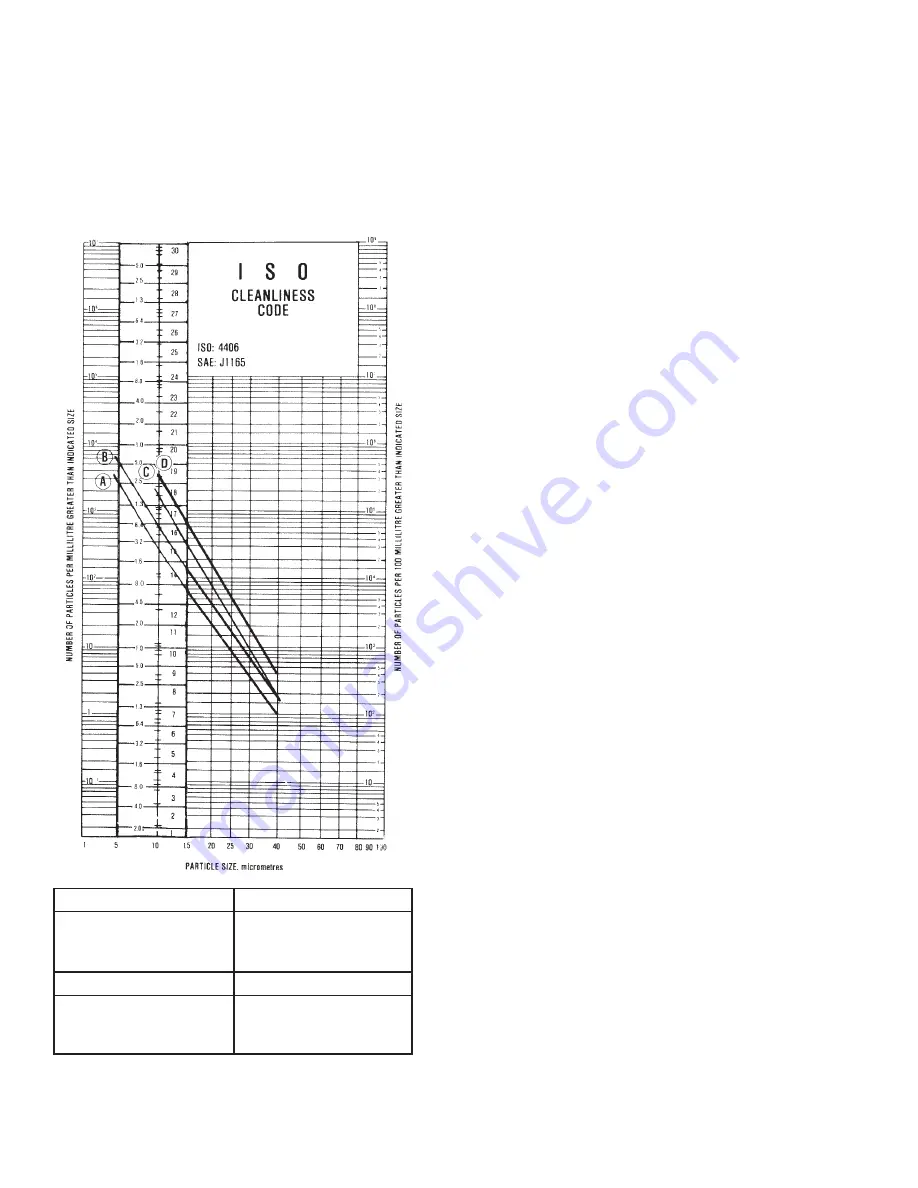
General contaminant levels have been developed
based on this experience and are shown in Figure
32.
Acceptable contamination levels at machine start
up for the system loop should be equal to or better
than Curve D. The machine may be exercised to
500 psi but should not be worked (pressure over
500 psi) until the oil cleanliness meets or exceeds
Curve C.
The machine should clean up during a relatively
short period of normal operation to meet the oil
cleanliness level of Curve A or Curve B. A system
that meets Curve A will provide the user with a
longer trouble-free operating life than one that
meets Curve B. The Curve A cleanliness level
should be met in systems exceeding the continuous
pressure limit for 1000 hours/years machine use.
Some control valves may require better
contamination limits than specified in
Figure 98.
Controls with small area screens or low force level
values may be susceptible to malfunction from
contamination.
The contamination sensitivity of components
generally increases with higher pressure,
temperature or speed. A better fluid contaminant
profile may be required for systems which operate
near the extremes of their ratings. Short life or
infrequent operation requirements may increase
allowable contaminants.
Figure 95. Fluid Cleanliness Chart
Curve A
Curve C
Desired limit for longer
Limit at machine ship
life (3500 PSI continuous
and new fluid added to
system pressure)
transmission
Curve B
Curve D
Continuous operating
Limit at machine start up
limit (2000 PSI continuous
pressure) system
The selection of a filter depends on a number of
factors including the contaminant ingression rate,















































