VigorBX 2000 Series User’s Guide
474
Scheduling: Based on classification of service level to assign packets to queues and
associated service types
The basic QoS implementation in Vigor routers is to classify and schedule packets based on
the service type information in the IP header. For instance, to ensure the connection with the
headquarter, a teleworker may enforce an index of QoS Control to reserve bandwidth for
HTTPS connection while using lots of application at the same time.
One more larger-scale implementation of QoS network is to apply DSCP (Differentiated
Service Code Point) and IP Precedence disciplines at Layer 3. Compared with legacy IP
Precedence that uses Type of Service (ToS) field in the IP header to define 8 service classes,
DSCP is a successor creating 64 classes possible with backward IP Precedence compatibility. In
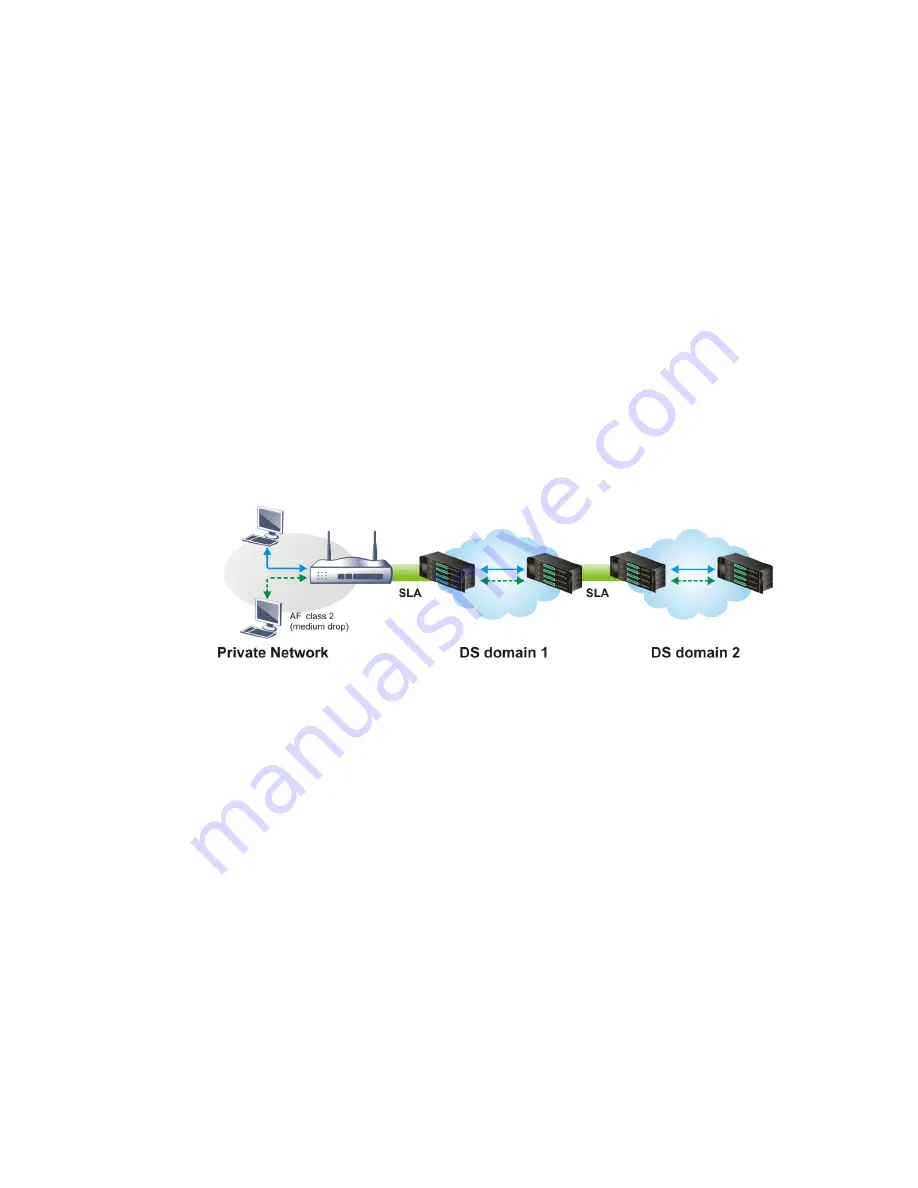
a QoS-enabled network, or Differentiated Service (DiffServ or DS) framework, a DS domain
owner should sign a Service License Agreement (SLA) with other DS domain owners to define
the service level provided toward traffic from different domains. Then each DS node in these
domains will perform the priority treatment. This is called per-hop-behavior (PHB). The
definition of PHB includes Expedited Forwarding (EF), Assured Forwarding (AF), and Best
Effort (BE). AF defines the four classes of delivery (or forwarding) classes and three levels of
drop precedence in each class.
Vigor routers as edge routers of DS domain shall check the marked DSCP value in the IP header
of bypassing traffic, to allocate certain amount of resource execute appropriate policing,
classification or scheduling. The core routers in the backbone will do the same checking
before executing treatments in order to ensure service-level consistency throughout the
whole QoS-enabled network.
However, each node may take different attitude toward packets with high priority marking
since it may bind with the business deal of SLA among different DS domain owners. It’s not
easy to achieve deterministic and consistent high-priority QoS traffic throughout the whole
network with merely Vigor router’s effort.
Summary of Contents for VigorBX 2000 Series
Page 1: ......
Page 12: ......
Page 62: ...VigorBX 2000 Series User s Guide 50 This page is left blank ...
Page 122: ...VigorBX 2000 Series User s Guide 110 ...
Page 145: ...VigorBX 2000 Series User s Guide 133 ...
Page 163: ...VigorBX 2000 Series User s Guide 151 ...
Page 180: ...VigorBX 2000 Series User s Guide 168 ...
Page 222: ...VigorBX 2000 Series User s Guide 210 This page is left blank ...
Page 248: ...VigorBX 2000 Series User s Guide 236 This page is left blank ...
Page 330: ...VigorBX 2000 Series User s Guide 318 This page is left blank ...
Page 419: ...VigorBX 2000 Series User s Guide 407 ...
Page 428: ...VigorBX 2000 Series User s Guide 416 The items categorized under OTHERS ...
Page 454: ...VigorBX 2000 Series User s Guide 442 This page is left blank ...
Page 467: ...VigorBX 2000 Series User s Guide 455 ...
Page 532: ...VigorBX 2000 Series User s Guide 520 This page is left blank ...
Page 574: ...VigorBX 2000 Series User s Guide 562 This page is left blank ...
Page 597: ...VigorBX 2000 Series User s Guide 585 ...
Page 604: ...VigorBX 2000 Series User s Guide 592 ...
Page 608: ...VigorBX 2000 Series User s Guide 596 ...
Page 610: ...VigorBX 2000 Series User s Guide 598 This page is left blank ...