65
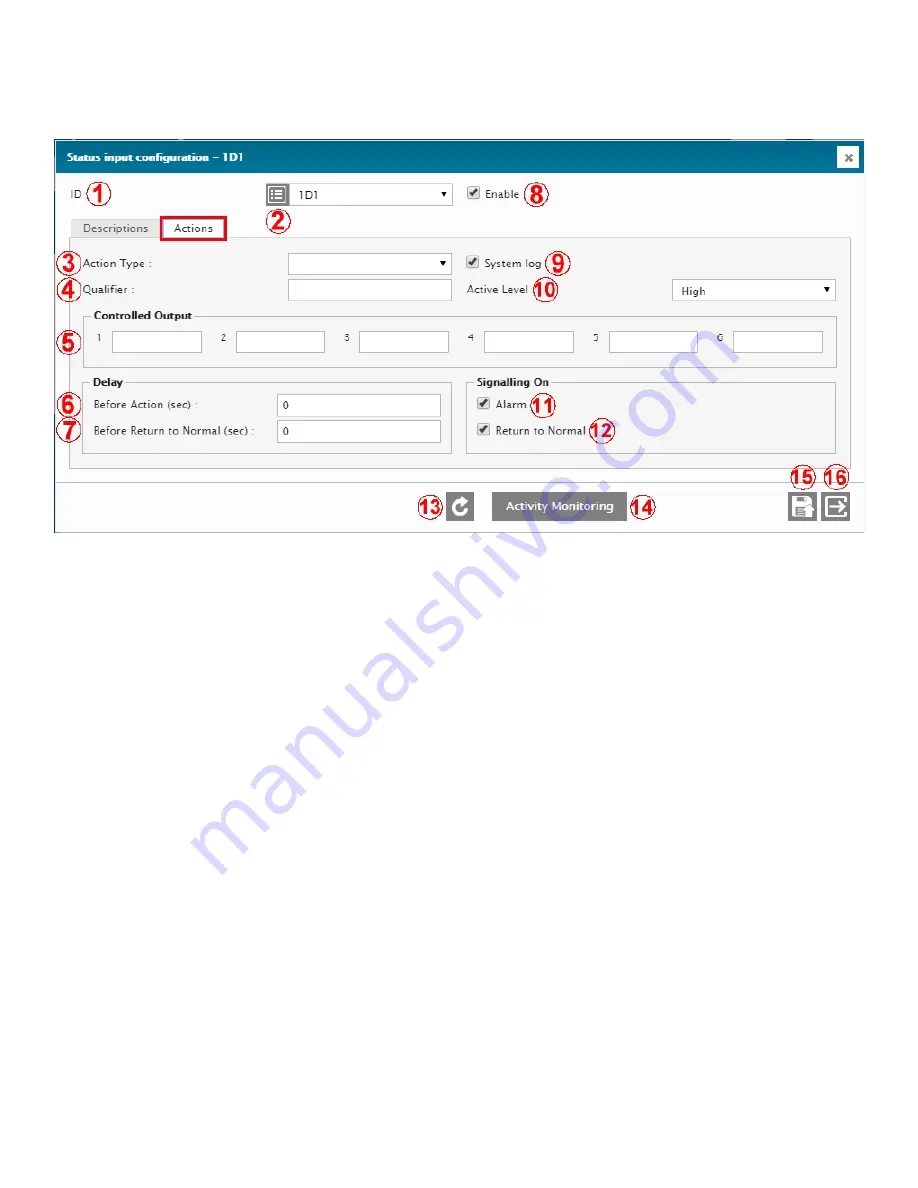
Status input configuration menu
1 –
ID
ID of the selected input. Select from the drop-down menu.
2 –
I/O DESCRIPTION RETRIEVAL
Click to retrieve and display the current normal description of that ID. Normally hidden to minimize data transfers
on low speed or high fee data connections.
3 –
ACTION TYPE
Selects the action type that will happen when an out-of-limit condition occurs. 3 types are available: Major alarm,
Minor alarm, and Command (CMD). On CMD, no alarm will be triggered. Use this Action when you want to take
actions without triggering any alarms.
4 –
QUALIFIER
Qualifying element (operand) which can be any input, output, flag, timer, SNMP GET, Logic Gate, etc. Essentially
any ID in the Cortex can be used to mute or unmute the input to prevent it from taking any action. When the Qualifier
is active, the input will be monitored and be able to generate alarms. When the qualifier is non-active (or normal),
the input will be muted and it will not be able to generate an alarm. To invert the Qualifier’s level, simply put a ! in
front of its ID. For example, use !1D01 to invert it. Leave the Qualifier field blank for a “don’t care” condition.
5 –
CONTROLLED OUTPUT
Outputs to be controlled (on/off) based on the state of this input. The two output types allowed are relays (both
physical and virtual) and SNMP SETs. For the relays, adding a P suffix will Pulse the relay (ex: 1R01P), L will Latch
it and R will Release it.
6 –
DELAY BEFORE ACTION
Delay before the input changes into an active state when an out-of-limit condition occurs. Prevents glitches from
setting-off any alarms.
7 –
DELAY BEFORE RETURN TO NORMAL
Delay before the input returns to a normal state once an out-of-limit condition is over. Prevents too-brief returns-to-
normal from causing multiple repeated alarms.
8 –
ENABLE
Enable / disable the input. Useful to deactivate an input, without losing all its settings, when the input is causing
intermittent problems or nuisance alarms.
9 –
SYSTEM LOG
















































