VRRP
Overview
Cisco 500 Series Stackable Managed Switch Administration Guide
441
24
Router B and C function as a
virtual router backups
. If the virtual router master
fails, the router configured with the higher priority becomes the virtual router
master and provides service to the LAN hosts with minimal interruption.
NOTE
The VRRP router priority depends on the following: If the VRRP router
is the owner, its priority is 255 (the highest), if it is not an owner, the priority is
manually configured (always less than 255).
When Router A recovers, it becomes the virtual router master again. During the
period that the master is recovering, both masters will forward packets and as a
result, there is some duplication (regular behavior) but no interruption.
For more detail on the roles that VRRP routers play and what happens if the virtual
router master fails, see the
VRRP Router Priority and Preemption
section.
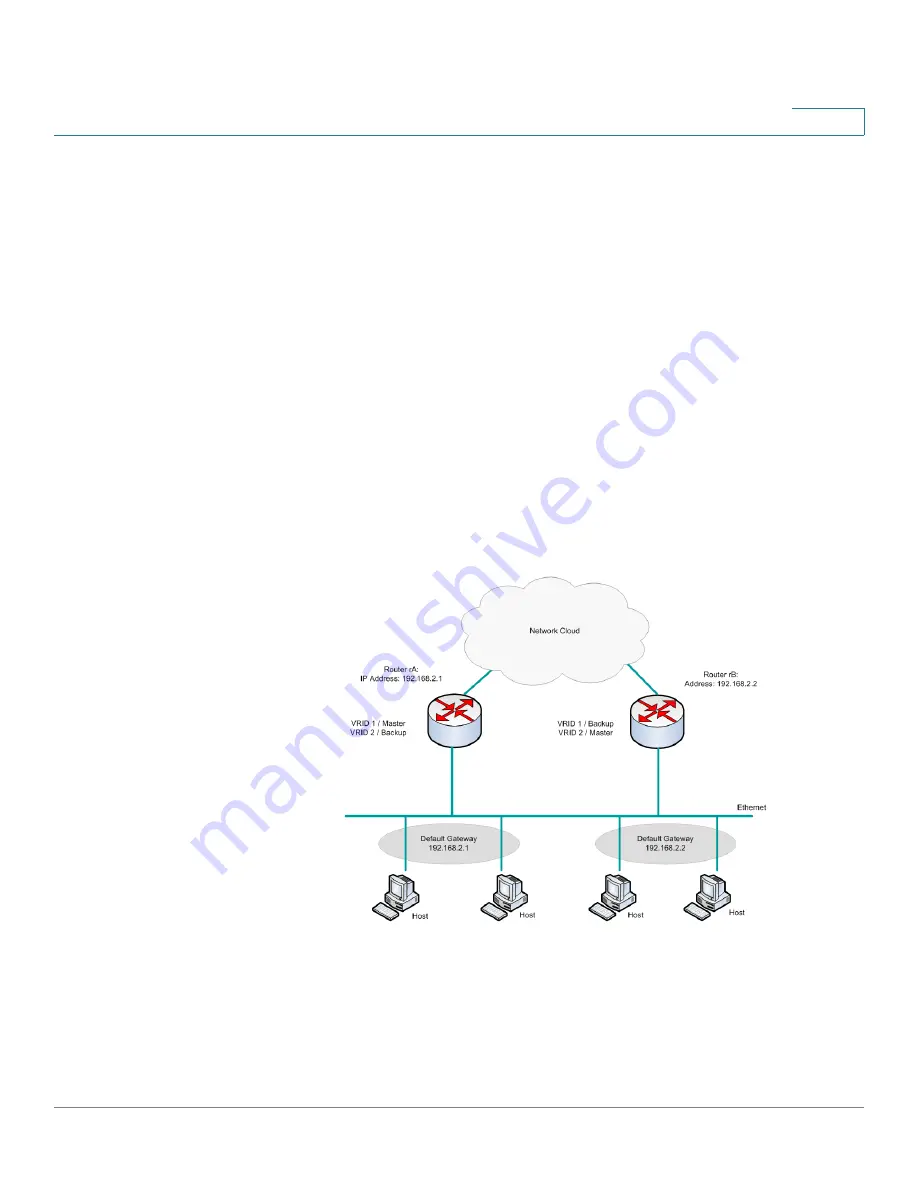
Figure 15
shows a LAN topology in which VRRP is configured. Routers A and B
share the traffic to and from clients 1 through 4 and Routers A and B act as virtual
router backups to each other if either router fails.
Figure 15 Load Sharing VRRP Topology
In this topology, two virtual routers are configured. For virtual router 1, rA is the
owner of IP address 192.168.2.1 and is the virtual router master, and rB is the virtual
router backup to rA. Clients 1 and 2 are configured with the default gateway IP
address of 192.168.2.1.
















































