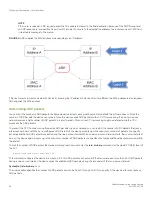
NOTE
You also can bias the Layer 3 switch to select one of the routes by configuring them with different administrative distances.
However, make sure you do not give a static route a higher administrative distance than other types of routes, unless you want
those other types to be preferred over the static route.
The steps for configuring the static routes are the same as described in the previous section. The following sections provide examples.
To configure multiple static IP routes, enter commands such as the following.
device(config)# ip route 10.128.2.69 255.255.255.0 10.157.22.1
device(config)# ip route 10.128.2.69 255.255.255.0 10.111.10.1
The commands in the previous example configure two static IP routes. The routes go to different next-hop gateways but have the same
metrics. These commands use the default metric value (1), so the metric is not specified. These static routes are used for load sharing
among the next-hop gateways.
The following commands configure static IP routes to the same destination, but with different metrics. The route with the lowest metric is
used by default. The other routes are backups in case the first route becomes unavailable. The Layer 3 switch uses the route with the
lowest metric if the route is available.
device(config)# ip route 10.128.2.69 255.255.255.0 10.157.22.1
device(config)# ip route 10.128.2.69 255.255.255.0 10.111.10.1 2
device(config)# ip route 10.128.2.69 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.1 3
In this example, each static route has a different metric. The metric is not specified for the first route, so the default (1) is used. A metric is
specified for the second and third static IP routes. The second route has a metric of two and the third route has a metric of 3. Thus, the
second route is used only of the first route (which has a metric of 1) becomes unavailable. Likewise, the third route is used only if the first
and second routes (which have lower metrics) are both unavailable.
Configuring standard static IP routes and interface or null static routes to the same destination
You can configure a null0 or interface-based static route to a destination and also configure a normal static route to the same destination,
so long as the route metrics are different.
When the Layer 3 switch has multiple routes to the same destination, the Layer 3 switch always prefers the route with the lowest metric.
Generally, when you configure a static route to a destination network, you assign the route a low metric so that the Layer 3 switch prefers
the static route over other routes to the destination.
This feature is especially useful for the following configurations. These are not the only allowed configurations but they are typical uses of
this enhancement:
•
When you want to ensure that if a given destination network is unavailable, the Layer 3 switch drops (forwards to the null
interface) traffic for that network instead of using alternate paths to route the traffic. In this case, assign the normal static route to
the destination network a lower metric than the null route.
•
When you want to use a specific interface by default to route traffic to a given destination network, but want to allow the Layer 3
switch to use other interfaces to reach the destination network if the path that uses the default interface becomes unavailable. In
this case, give the interface route a lower metric than the normal static route.
NOTE
You cannot add a null or interface-based static route to a network if there is already a static route of any type with the same
metric you specify for the null or interface-based route.
In the example, two static routes configured for the same destination network. One of the routes is a standard static route and has a
metric of 1. The other static route is a null route and has a higher metric than the standard static route. The Layer 3 switch always prefers
the static route with the lower metric. In this example, the Layer 3 switch always uses the standard static route for traffic to destination
network 192.168.7.0/24, unless that route becomes unavailable, in which case the Layer 3 switch sends traffic to the null route instead.
Configuring IP parameters - Layer 3 switches
FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing
68
53-1003627-04
Summary of Contents for FastIron SX 1600
Page 2: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 2 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 16: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 16 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 20: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 20 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 142: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 142 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 150: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 150 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 200: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 200 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 214: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 214 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 350: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 350 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 476: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 476 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 588: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 588 53 1003627 04 ...