ARP parameter configuration
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a standard IP protocol that enables an IP Layer 3 switch to obtain the MAC address of another
device interface when the Layer 3 switch knows the IP address of the interface. ARP is enabled by default and cannot be disabled.
NOTE
Brocade Layer 2 switches also support ARP. However, the configuration options described later in this section apply only to
Layer 3 switches, not to Layer 2 switches.
How ARP works
A Layer 3 switch needs to know a destination MAC address when forwarding traffic, because the Layer 3 switch encapsulates the IP
packet in a Layer 2 packet (MAC layer packet) and sends the Layer 2 packet to a MAC interface on a device directly attached to the
Layer 3 switch. The device can be the packet final destination or the next-hop router toward the destination.
The Layer 3 switch encapsulates IP packets in Layer 2 packets regardless of whether the ultimate destination is locally attached or is
multiple router hops away. Because the Layer 3 switch IP route table and IP forwarding cache contain IP address information but not
MAC address information, the Layer 3 switch cannot forward IP packets based solely on the information in the route table or forwarding
cache. The Layer 3 switch needs to know the MAC address that corresponds with the IP address of either the packet locally attached
destination or the next-hop router that leads to the destination.
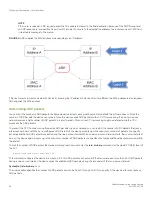
For example, to forward a packet whose destination is multiple router hops away, the Layer 3 switch must send the packet to the next-
hop router toward its destination, or to a default route or default network route if the IP route table does not contain a route to the packet
destination. In each case, the Layer 3 switch must encapsulate the packet and address it to the MAC address of a locally attached device,
the next-hop router toward the IP packet destination.
To obtain the MAC address required for forwarding a datagram, the Layer 3 switch first looks in the ARP cache (not the static ARP table)
for an entry that lists the MAC address for the IP address. The ARP cache maps IP addresses to MAC addresses. The cache also lists the
port attached to the device and, if the entry is dynamic, the age of the entry. A dynamic ARP entry enters the cache when the Layer 3
switch receives an ARP reply or receives an ARP request (which contains the sender IP address and MAC address). A static entry enters
the ARP cache from the separate static ARP table when the interface for the entry comes up.
To ensure the accuracy of the ARP cache, each dynamic entry has its own age timer. The timer is reset to zero each time the Layer 3
switch receives an ARP reply or ARP request containing the IP address and MAC address of the entry. If a dynamic entry reaches its
maximum allowable age, the entry times out and the software removes the entry from the table. Static entries do not age out and can be
removed only by you.
If the ARP cache does not contain an entry for the destination IP address, the Layer 3 switch broadcasts an ARP request out all its IP
interfaces. The ARP request contains the IP address of the destination. If the device with the IP address is directly attached to the Layer 3
switch, the device sends an ARP response containing its MAC address. The response is a unicast packet addressed directly to the Layer
3 switch. The Layer 3 switch places the information from the ARP response into the ARP cache.
ARP requests contain the IP address and MAC address of the sender, so all devices that receive the request learn the MAC address and
IP address of the sender and can update their own ARP caches accordingly.
NOTE
The ARP request broadcast is a MAC broadcast, which means the broadcast goes only to devices that are directly attached to
the Layer 3 switch. A MAC broadcast is not routed to other networks. However, some routers, including Brocade Layer 3
switches, can be configured to reply to ARP requests from one network on behalf of devices on another network.
Configuring IP parameters - Layer 3 switches
FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing
53-1003627-04
53
Summary of Contents for FastIron SX 1600
Page 2: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 2 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 16: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 16 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 20: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 20 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 142: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 142 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 150: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 150 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 200: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 200 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 214: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 214 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 350: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 350 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 476: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 476 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 588: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 588 53 1003627 04 ...