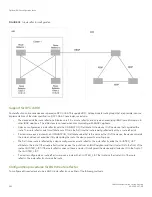
NOTE
All configuration for route reflection takes place on the route reflectors, not on the
clients.
Enter the following commands to configure a Brocade device as route reflector 1. To configure route reflector 2, enter the same
commands on the device that will be route reflector 2. The clients require no configuration for route reflection.
device(config-bgp)# cluster-id 1
Syntax:
[no] cluster-id
num
|
ip-addr
The
num
and
ip-addr
parameters specify the cluster ID and can be a number from 1 - 4294967295, or an IP address. The default is
the device ID. You can configure one cluster ID on the device. All route-reflector clients for the device are members of the cluster.
NOTE
If the cluster contains more than one route reflector, you need to configure the same cluster ID on all the route reflectors in the
cluster. The cluster ID helps route reflectors avoid loops within the cluster.
To add an IBGP neighbor to the cluster, enter the following command:
device(config-bgp)# neighbor 10.0.1.0 route-reflector-client
Syntax:
[no] neighbor
ip-addr
route-reflector-client
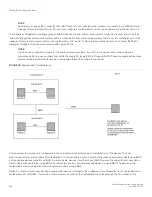
Disabling or re-enabling client-to-client route reflection
By default, the clients of a route reflector are not required to be fully meshed. Routes from a client are reflected to other clients. However,
if the clients are fully meshed, route reflection is not required between clients.
If you need to disable route reflection between clients, enter the
no client-to-client-reflection
command. When this feature is disabled,
route reflection does not occur between clients does still occur between clients and non-clients.
device(config-bgp-router)# no client-to-client-reflection
Enter the following command to re-enable the feature.
device(config-bgp)# client-to-client-reflection
Syntax:
[no] client-to-client-reflection
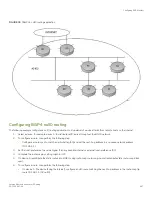
Configuring confederations
A
confederation
is a BGP4 Autonomous System (AS) that has been subdivided into multiple, smaller autonomous systems. Subdividing
an AS into smaller autonomous systems simplifies administration and reduces BGP4-related traffic, which in turn reduces the complexity
of the Interior Border Gateway Protocol (IBGP) mesh among the BGP4 devices in the AS.
The Brocade implementation of this feature is based on RFC 3065.
Normally, all BGP4 devices within an AS must be fully meshed, so that each BGP4 device has BGP4 sessions to all the other BGP4
devices within the AS. This is feasible in smaller autonomous systems, but becomes unmanageable in autonomous systems containing
many BGP4 devices.
When you configure BGP4 devices into a confederation, all the devices within a sub-AS (a subdivision of the AS) use IBGP and must be
fully meshed. However, devices use EBGP to communicate between different sub-autonomous systems.
Optional BGP4 configuration tasks
FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing
53-1003627-04
391
Summary of Contents for FastIron SX 1600
Page 2: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 2 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 16: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 16 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 20: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 20 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 142: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 142 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 150: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 150 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 200: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 200 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 214: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 214 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 350: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 350 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 476: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 476 53 1003627 04 ...
Page 588: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 588 53 1003627 04 ...