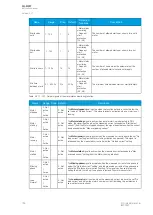
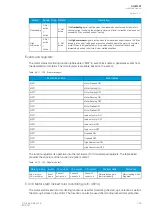
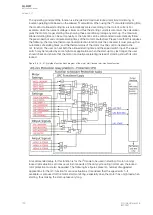
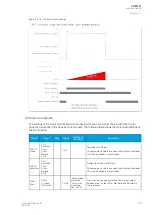
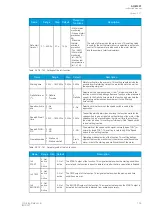
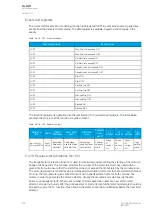
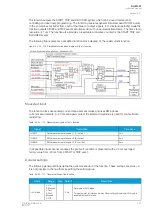
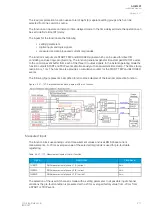
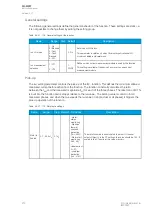
The frequent start protection function in a motor protection module operates with the motor status
monitoring function and follows the motor data set there. Motor starting is monitored internally (MST
signal out) in the N> function. The user only needs to activate the N> function and then do the
following: set the number of allowed starts for hot and cold situations, set the minimum time between
consequent starts, and set the limits of "Hot" and "Cold" situations. The thermal overload function also
needs to be activated and set, if the user wants to use the hot and cold motor status separation.
Figure. 5.4.19 - 103. Simplified function block diagram of the N> function.
The operating principle of the frequent start protection function is to calculate an equivalent start
stress in each start; the calculation is based on the set starts per hour and the safe stall time settings
(hot and cold) regardless of the actual start duration. In each start attempt the function does the
following calculation: a time equal to the safe stall time and is added to the starts counter, and the
quotient of the safe stall time divided by the set starts time (in hours) is then subtracted from this sum.
This way the start counter can be applied to follow the motor's thermal status and the number of starts
per hour accurately.
A
AQ
Q-M257
-M257
Instruction manual
Version: 2.07
© Arcteq Relays Ltd
IM00021
201
Summary of Contents for AQ-M257
Page 1: ...AQ M257 Motor protection IED Instruction manual...
Page 2: ......