Functions and setup of the contrAA 600
24
Edition 01/2014
contrAA 600
5
Functions and setup of the contrAA 600
5.1
Physical measuring principle HR-CS AAS
The measuring principle of the High Resolution Continuum Source atomic absorption spec-
trometry (HR-CS AAS) as well as the traditional line radiator AAS (LS AAS) is the absorption
of a primary radiation by means of analyte atoms in the base state. In this, the absorption
signal is a measure for the concentration of the relevant element in the analyzed sample.
Each AAS device consists of the following basic components:
Radiation source
Atomizer
Monochromator
Detector
Evaluation unit (PC)
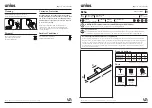
Fig. 5
Schematic comparison of the physical measuring principle of LS AAS and HR-CS
AAS
Radiation source
In the HR-CS AAS the element-specific radiation source of the traditional AAS (hollow cath-
ode lamp, HCL) is replaced by a single continuum source for all elements and lines - a
Xenon short arc lamp. The special electrode geometry of the Xenon short arc lamp creates a
hot focal spot (hot spot), which guarantees a very high radiation density and seamless
emission over the whole spectral range (190 - 900 nm). This means that all analysis lines of
interest are available at any time - both resonance wavelengths of the analysis elements and
secondary wavelengths without technical restrictions due to HCL specifics such as outlet
window and emission intensity. In addition, absorption lines and absorption bands of diatom-
ic molecules (PO, CS,...) may be used for analytic element determination.
Atomizer
The following atomization techniques are displayed on the contrAA 600:
Graphite tube technique for liquid samples
Graphite tube technique for solid samples
HydrEA technique as coupling between hydride and graphite tube techniques