Industry Cellular Gateway
4.1.3 Modbus
Modbus is one of the most popular automation protocols in the world, supporting traditional RS-232/422/485
devices and recently developed Ethernet devices. Many industrial devices, such as PLCs, DCSs, HMIs,
instruments, and smart meters, use Modbus protocol as the communication standard. It is used to establish
master-slave communication between intelligent devices.
However, the Ethernet-based Modbus protocol is so different from the original serial-based protocols. In order
to integrate Modbus networks, the IoT Gateway, including one or more serial ports that support RS-232 and
RS-485 communication interface, can automatically and intelligently translate between Modbus TCP (Ethernet)
and Modbus RTU/ASCII (serial) protocols, allowing Ethernet-based PLCs to control instruments over RS-485
without additional programming or effort.
NOTE: When Modbus devices are connected to/under the same serial port of IoT Modbus Gateway, those
Modbus devices must use the same protocol with the same configuration (i.e., either Modbus RTU or Modbus
ASCII with same Baud Rate setting).
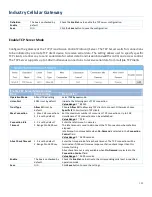
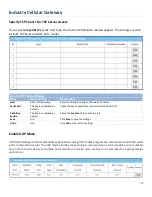
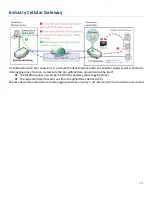
Modbus Gateway Scenario
The IoT Gateway serves as a Modbus gateway to
communicate with the Modbus TCP Master, the SCADA
Server, located at remote control center for Modbus
device accessing.
The Modbus TCP Master requests the IoT Gateway for
Modbus devices' information, e.g., Data Acquisition or
Register/Value Modification, via general Internet
accessing, and the IoT Gateway serves as the gateway
for data forwarding.
Under such configuration, the Modbus TCP Master
requests the information from or sending control
commands to various Modbus/RTU Slave devices that
attached to the Modbus Gateway. And the Modbus
gateway executes corresponding processes and replies
the Modbus/TCP Master with the results.
194