Chapter 5: IP Core Architecture
5–13
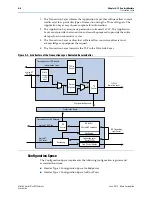
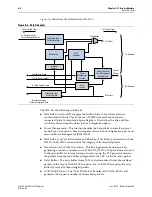
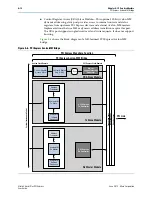
PCI Express Avalon-MM Bridge
June 2012
Altera Corporation
Stratix V Hard IP for PCI Express
The bridge has the following additional characteristics:
■
Type 0 and Type 1 vendor-defined incoming messages are discarded
■
Completion-to-a-flush request is generated, but not propagated to the interconnect
fabric
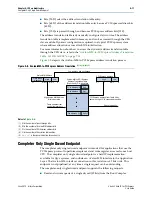
Each PCI Express base address register (BAR) in the Transaction Layer maps to a
specific, fixed Avalon-MM address range. You can use separate BARs to map to
various Avalon-MM slaves connected to the RX Master port.
The following sections describe the supported modes of operation:
■
Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Write Requests
■
Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Upstream Read Requests
■
PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Read Completions
■
PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Downstream Write Requests
■
PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Downstream Read Requests
■
PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Read Completions
■
Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Address Translation
■
PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Address Translation
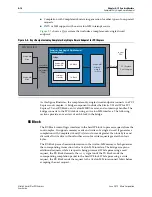
Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Write Requests
The Avalon-MM bridge accepts Avalon-MM burst write requests with a burst size of
up to 512 Bytes at the Avalon-MM TX slave interface. The Avalon-MM bridge
converts the write requests to one or more PCI Express write packets with 32– or
64-bit addresses based on the address translation configuration, the request address,
and the maximum payload size.
The Avalon-MM write requests can start on any address in the range defined in the
PCI Express address table parameters. The bridge splits incoming burst writes that
cross a 4 KByte boundary into at least two separate PCI Express packets. The bridge
also considers the root complex requirement for maximum payload on the PCI
Express side by further segmenting the packets if needed.
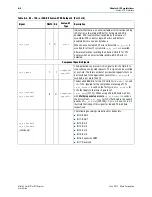
The bridge requires Avalon-MM write requests with a burst count of greater than one
to adhere to the following byte enable rules:
■
The Avalon-MM byte enable must be asserted in the first qword of the burst.
■
All subsequent byte enables must be asserted until the deasserting byte enable.
■
The Avalon-MM byte enable may deassert, but only in the last qword of the burst.
1
To improve PCI Express throughput, Altera recommends using an Avalon-MM burst
master without any byte-enable restrictions.
Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Upstream Read Requests
The PCI Express Avalon-MM bridge converts read requests from the system
interconnect fabric to PCI Express read requests with 32-bit or 64-bit addresses based
on the address translation configuration, the request address, and the maximum read
size.