User’s Manual MSO/UPO2000 Seri es
93 / 137
Instruments.uni-trend.com
master and slave computer. The bus is a multiple master bus that prevents data corruption through conflict
detection and arbitration mechanisms. It is worth noting that the I
2
C bus has two address bit widths, 7 bits
and 10 bits, where 10 bits and 7 bits addresses are compatible that can be used in combination. When the bus
is idle, both lines are high level. When any device on the bus output low level, it will make the bus signal goes
low, i.e., the signals of multiple devices are " wired and" logic. This special logic relation is the key to bus
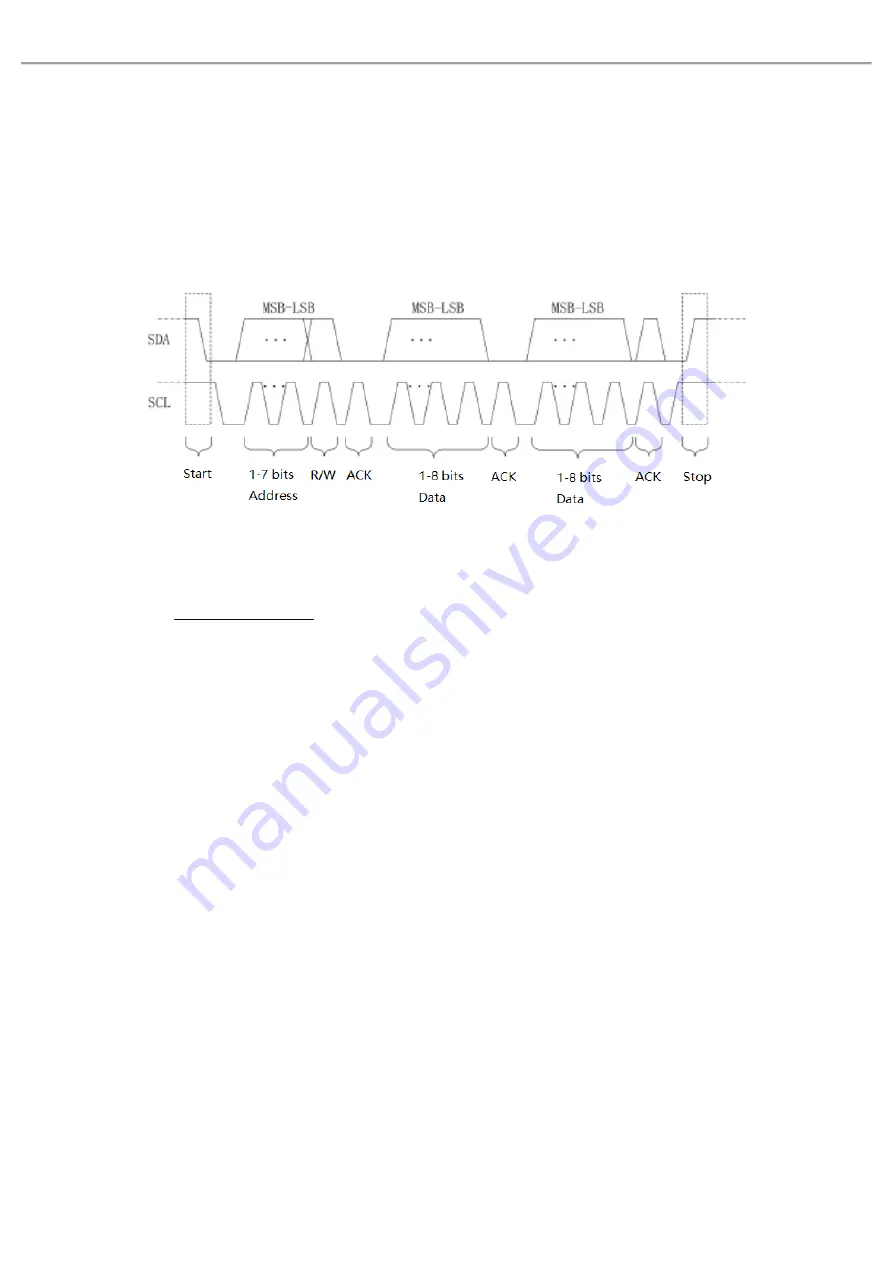
arbitration. The protocol requires that the data SDA must remain stable while the clock line SCL is high, and
the data is usually transmitted in MSB form. As shown in Figure 14-2.
Figure 14-2
(1)
Bus Decoding
Refer to
(2)
SCL SOURCE
Select SCL source to any one of CH1
~
CH4 or D0-D15 to be clock input of I
2
C.
(3)
SDA Source
Select SDA source to any one of CH1
~
CH4 or D0-D15 to be data input of I
2
C.
14.3 SPI Decoding
SPI (serial peripheral interface) can connect the host with peripheral equipment in serial way to
communication. It’s full duplex and synchronous communication bus. It’s usually use 4 signal connecting
line, MOSI: master data output, slave data input; MISO: master input, slave data output; SCLK: clock
signal generated by master; CS: chip select enable signal from slave.
SPI interface is mainly used for synchronous serial data transfer between the host and low-speed
peripheral equipment. Under the shift pulse of the host, the data is transferred bit by bit, the high bit in
front and behind is the low bit. SPI interface is widely used because it does not require slave address
addressing, which is full duplex communication and the protocol is simple. SPI protocol transmission as
shown in Figure 14-3.
















































