13.5.6 Configuring the SBI as a Transmitter or a Receiver
Setting SBICR2<TRX> to "1" configures the SBI as a transmitter. Setting <TRX> to "0" configures the
SBI as a receiver.
At the slave mode:
・
when data is transmitted in the addressing format.
・
when the received slave address matches the value specified at SBII2CAR.
・
when a general-call address is received; i.e., the eight bits following the start condition are all zeros.
If the value of the direction bit (R/W) is "1", <TRX> is set to "1" by the hardware. If the bit is "0",
<TRX> is set to "0".
As a master device, the SBI receives acknowledgement from a slave device. If the direction bit of "1" is trans-
mitted, <TRX> is set to "0" by the hardware. If the direction bit is "0", <TRX> changes to "1". If the SBI
does not receive acknowledgement, <TRX> retains the previous value.
<TRX> is cleared to "0" by the hardware when it detects the stop condition on the bus or the arbitration
lost.
If SBI is used in free data format, <TRX> is not changed by the hardware.
13.5.7 Configuring the SBI as a Master or a Slave
Setting SBICR2<MST> to "1" configures the SBI to operate as a master device.
Setting <MST> to "0" configures the SBI as a slave device. <MST> is cleared to "0" by the hardware
when it detects the stop condition on the bus or the arbitration lost.
13.5.8 Generating Start and Stop Conditions
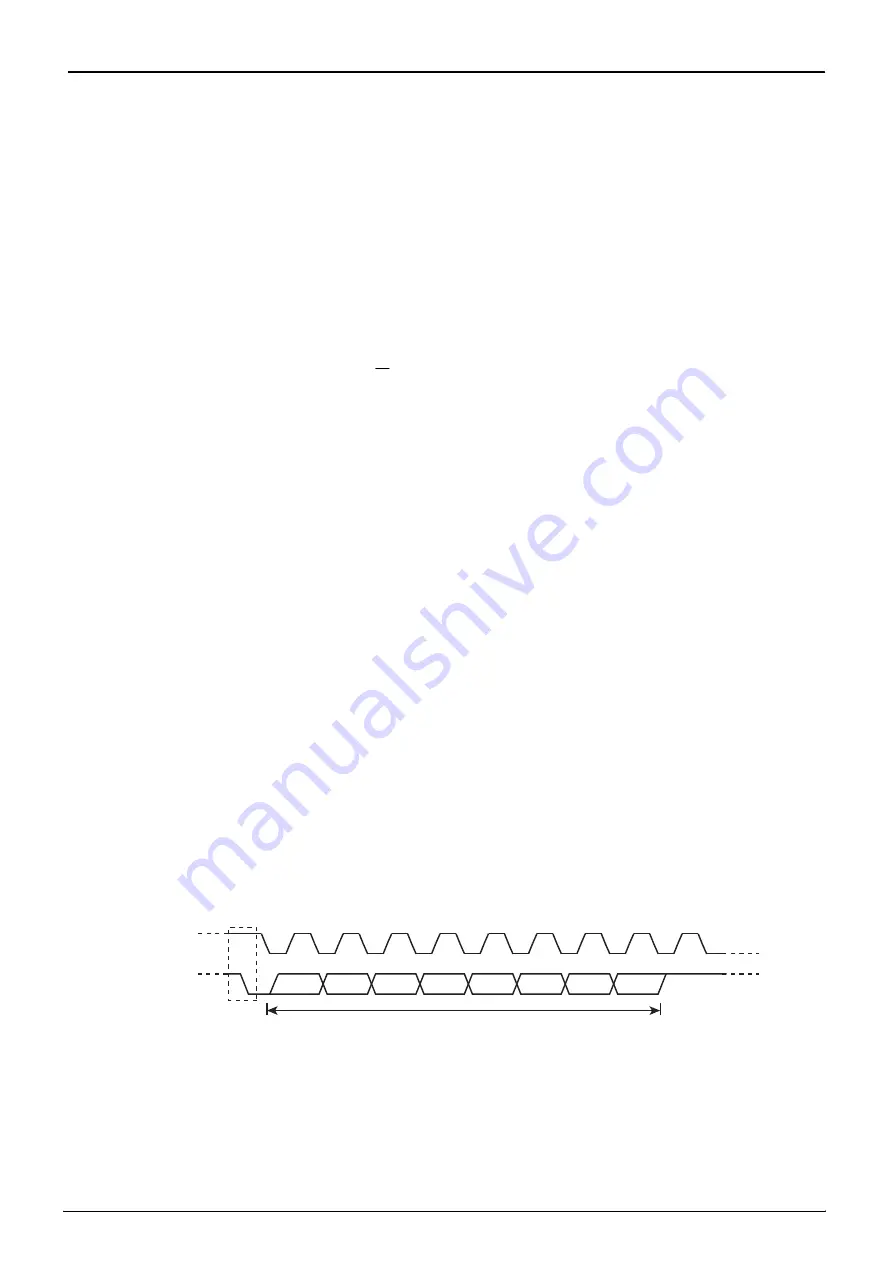
When SBISR<BB> is "0", writing "1" to SBICR2<MST, TRX, BB, PIN> causes the SBI to start a se-
quence for generating the start condition and to output the slave address and the direction bit prospectively writ-
ten in the data buffer register. <ACK> must be set to "1" in advance.
Slave address and direction bit
Start condition
Acknowledgement signal
A6
A5
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
R/W
1
SCL pin
SDA pin
Figure 13-5 Generating the Start Condition and a Slave Address
When <BB> is "1", writing "1" to <MST, TRX, PIN> and "0" to <BB> causes the SBI to start a sequence
for generating the stop condition on the bus. The contents of <MST, TRX, BB, PIN> should not be altered un-
til the stop condition appears on the bus.
TMPM3V6/M3V4
13. Serial Bus Interface (I2C/SIO)
13.5 Control in the I2C Bus Mode
Page 282
2019-02-06
Содержание TMPM3V4
Страница 1: ...32 Bit RISC Microcontroller TX03 Series TMPM3V6 M3V4 ...
Страница 2: ... 2019 Toshiba Electronic Devices Storage Corporation ...
Страница 7: ...Revision History Date Revision Comment 2019 02 06 1 First Release ...
Страница 8: ......
Страница 22: ...xiv ...
Страница 52: ...TMPM3V6 M3V4 3 Processor Core 3 6 Exclusive access Page 30 2019 02 06 ...
Страница 148: ...TMPM3V6 M3V4 7 Exceptions 7 6 Exception Interrupt Related Registers Page 126 2019 02 06 ...
Страница 178: ...TMPM3V6 M3V4 9 Input Output port 9 2 Block Diagrams of Ports Page 156 2019 02 06 ...
Страница 206: ...TMPM3V6 M3V4 10 16 bit Timer Event Counters TMRB 10 7 Applications using the Capture Function Page 184 2019 02 06 ...
Страница 232: ...TMPM3V6 M3V4 11 Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter Circuit UART 11 4 Operation Description Page 210 2019 02 06 ...
Страница 354: ...TMPM3V6 M3V4 14 Synchronous Serial Port SSP 14 6 Frame Format Page 332 2019 02 06 ...
Страница 419: ...TMPM3V6 M3V4 Page 397 2019 02 06 ...
Страница 420: ...TMPM3V6 M3V4 16 Analog Digital Converter ADC 16 6 Timing chart of AD conversion Page 398 2019 02 06 ...
Страница 462: ...TMPM3V6 M3V4 21 Watchdog Timer WDT 21 5 Control register Page 440 2019 02 06 ...
Страница 510: ...TMPM3V6 M3V4 22 Flash Memory Operation 22 4 Programming in the User Boot Mode Page 488 2019 02 06 ...
Страница 538: ...TMPM3V6 M3V4 25 Electrical Characteristics 25 7 Recommended Oscillation Circuit Page 516 2019 02 06 ...
Страница 541: ...26 3 TMPM3V4FWUG TMPM3V4FSUG Type LQFP64 P 1010 0 50E LPHQVLRQV TMPM3V6 M3V4 Page 519 2019 02 06 ...
Страница 544: ......
















































