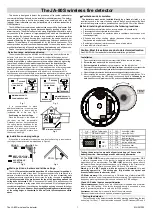
Operating Instructions— Type 323
Beam—The electron beam emitted by the cathode of a
CRT. Its impinging on the phosphor creates the light on
the face of the cathode-ray tube.
Bezel—The flange or cover which holds the external grati
cule, light filter, viewing hood, etc. in front of the cathode-
ray tube face.
Blanked— Condition under which the electron beam is pre
vented from striking the cathode-ray tube face.
Blanking—The process of creating the blanked condition.
Blooming—An increase in display size accompanying an
increase in CRT INTENSITY setting.
Calibration— Process whereby an instrument is adjusted to
perform within specified limits.
Characteristic Impedance— An ohmic value which expresses
an electrical quality of a transmission line or cable. It is
the impedance the line would present if if were of infinite
length.
Circuit Board—Any of various boards on which are mount
ed circuit components and inter-connections. The circuit board
is usually fastened to a chassis with screws or clips.
Compression— An increase in the deflection factor, usually
as the limits of the quality area are exceeded.
DC Balance—The condition existing in the Type 323 Oscillo
scope when, with the vertical input grounded, no trace shift
occurs as a result of any change in vertical deflection fac
tor.
DC Coupling—The condition existing when no capacitor
interrupts the path between the signal take-off point and
the oscilloscope circuit to which the signal is applied.
DC Reference Position—The position on the oscilloscope
graticule which is occupied by the trace when the input
is grounded. Normally refers to the vertical circuit, but
also pertains to the horizontal circuit during EXT HORIZ
operation.
Decoupling—The process of removing AC signals or tran
sients from the power supply voltages applied to a circuit.
Usually refers to shunting AC and transient signals to ground
by connecting a capacitor from the decoupling point to AC
ground, and an impedance between the power supply and
the decoupled point.
Deflection Blanking— Blanking by means of a deflection
structure in the cathode-ray tube electron gun which traps
the electron beam inside the gun to extinguish the spot,
permitting blanking during retrace and between sweeps,
regardless of intensity setting.
Deflection Factor—The ratio of the input signal amplitude
to the resultant displacement of the indicating spot (volts/
div).
Deflection Plates— Metal plates contained within a cathode-
ray tube. Application of voltage to these plates creates an
electro-static field which controls horizontal, vertical or
blanking deflection of the electron beam.
Deflection Polarity—The relation between signal polarity
and spot displacement direction. The Type 323 Oscilloscope
has a positive deflection polarity, indicating upward and
right deflection in response to + vertical and horizontal
input signals, respectively.
Deflection Sensitivity.—The div/volt ratio which describes
the amount of deflection resulting from a unit of applied
signal.
Differential Amplifier—An amplifier whose output signal is
proportional to the algebraic difference between 2 input
signals.
Differential Signal—The instantaneous algebraic difference
between two signals.
Display—The visual presentation created by the electron
beam on the face of a cathode-ray tube.
External Horizontal Signal— Any signal applied to the Type
323 Oscilloscope TRIG OR HORIZ INPUT connector for
purposes of EXT HORIZ oscilloscope operation.
External Trigger—Any signal applied to the Type 323 Os
cilloscope TRIG OR HORIZ INPUT connector for purposes
of EXT TRIG oscilloscope operation. Also the trigger gen
erated in response to this signal.
External Triggering— Introducing the triggering signal di
rectly into the trigger circuit from an external source.
Field Effect Transistor (FET)—A semi-conductor device whose
operation is analogous to a triode vacuum tube.
Free-Running Sweep—Continuously succesive sweeps occurring
independent of triggers or input signals.
Geometry—The degree to which a rectilinear display on a
CRT screen is accurately reproduced. Also the name of the
control which adjusts this quality.
Graticule— A scale associated with the cathode-ray tube
face.
Half-Power Point—The frequency at which the oscilloscope
response limits the display amplitude to 70.7% of the ac
tual voltage of the applied signal.
Holdoff—Sweep Holdoff.
Horizontal Amplifier—An amplifier for signals intended to
produce horizontal deflection.
Horizontal Deflection— Horizontal movement of the cathode-
ray tube electron beam away from its quiescent or no signal
position.
Horizontal Displacement—The amount of horizontal space
between electron beam quiescent position and instantaneous
position.
Horizontal Gain—The voltage ratio of output to input sig
nals associated with the Horizontal Amplifier.
Horizontal Sweep—The movement of the electron beam from
left to right across the cathode-ray tube face in response to
a changing horizontal amplifier voltage.
Input Coupling— Associated with the method of connect
ing a signal into a device or circuit. Usually refers to AC
or DC coupling and signal attenuation.
Input Impedance— The combination of R, C and I which a
® !
2-2
1
Содержание 323
Страница 4: ...Type 323 Fig 1 1 Type 323 Oscilloscope ...
Страница 14: ...Operating Instructions Type 323 2 2 Fig 2 1 External controls connectors and indicators ...
Страница 39: ...Circuit Description Type 323 3 4 Fig 3 3 Paraphase Am plifier simplified ...
Страница 51: ...Circuit Description Type 323 3 16 Fig 3 8 Blocking Oscillator simplified ...
Страница 71: ...Maintenance Type 323 4 15 Fig 4 13 Transistor data ...
Страница 72: ...Maintenance Type 323 4 16 Fig 4 14 M ain circuit board p a rtia l loft side vertical circuit components ...
Страница 147: ...T Y P E 3 2 3 O S C I L L O S C O P E B L O C K D IA G R A M MRI4 i ...
Страница 157: ...BL OCK DIAGRAM ...
Страница 158: ......
Страница 161: ...A TYPE 323 OSCILLOSCOPE ...
Страница 162: ...1 TYPE 323 OSCILLOSCOPE ...
Страница 163: ...FIG 2 CABINET ...
Страница 164: ...OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES 016 0119 00 1 POWER PACK 016 0112 00 1 COVER protective oscilloscope ...