Siemens Energy & Automation, Inc.
1 Introduction
1.1 Scope of Manual
This manual provides an overview for the installation, setup and
operation of the Siemens SIKOSTART 3RW35 controller.
Maintenance data consists of troubleshooting and spare parts
information. Note that the instructions in this manual do not
cover all details or variations in equipment, nor provide for every
possible contingency to be met in connection with installation,
operation, or maintenance.
1.2 SIKOSTART 3RW35 Features
The SIKOSTART 3RW35 product line is the next generation of
Siemens solid state reduced voltage controllers. This controller com-
bines DSP microprocessor and thyristor technologies to provide AC
induction motor starting and operation. The sturdy compact frame
affords rugged, industrial grade reliability.
The SIKOSTART 3RW35 controller is a dual ramp style controller
using phase control for the operation of three-phase induction
motors. Each unit includes soft start and stop parameters plus
fault detection. The controller can be used with an electro-
mechanical starter or, when combined with an overload relay,
the controller can be used as a solid-state starter.
The SIKOSTART 3RW35 controller is available as an open type
(compact frame, no enclosure) or in a NEMA 1, 3R, 4, or 12
enclosure. The unit can be ordered as a starter with overload
relays or as a combination starter with disconnecting means and
circuit overload protection devices. Additional options are also
available such as push buttons, pilot lights, and meters.
1.3 Applications and Potential Benefits
Typical applications for the SIKOSTART 3RW35 controller are to
soft start and soft stop AC induction motor driven equipment
such as fans, pumps and compressors. Applications may also
include controlling machines with gearbox, belt or chain drive
elements, such as: conveyors, sanders, planers, saws, packag-
ing machines and punch presses.
Using the SIKOSTART 3RW35 controller may provide benefits to
the drive system in the following ways:
1) the life of mechanical drive transmission elements is
extended, e.g., gearbox jerking is substantially reduced
resulting in less wear and tear;
2) reduced starting current relieves the supply network of cur-
rent peaks; and
3) smoother acceleration of loads eliminates process or product
damage.
2 Operating Principle
2.1 Function Overview
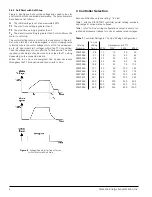
The SIKOSTART 3RW35 controller utilizes a voltage ramp design
to produce an output voltage to the motor that increases from a
customer selected initial voltage to full line supply voltage over
an adjustable starting time. This “voltage ramp” produces a
reduced current start (soft start) similar to a current limit start
without the load dependence of the current limit type start.
In addition to the voltage ramp feature, a constant voltage mode
is available which will further limit the starting current. This is
obtained by using the MAX START VOLTAGE adjustment,
Similarly, stopping time can be adjusted to provide a soft stop
for many pumping applications.
The SIKOSTART controller employs a DSP (digital signal proces-
sor) to control the motor. This advanced type of microprocessor
allows the controller to “contour” the starting and stopping
ramps. This contour adjusts for the nonlinearities of an induction
motor to produce a smoother and more linear motor start and
stop.
2.2 Functional Description
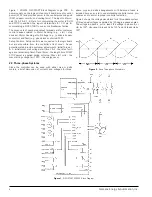
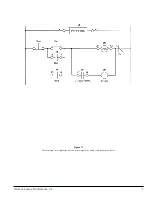
Power Poles. As is shown in the block diagram of figure 1, the
incoming main power (L1, L2, L3) is connected to the con-
troller’s three power poles which control the voltage to the
motor windings. Each power pole consists of two thyristors
(SCR’s) in a back-to-back arrangement for each phase which
allows alternating current to pass to the motor.
Snubber PCB. The snubber printed circuit board(s) contains the
trigger circuit for each SCR. The firing signal for each trigger cir-
cuit is generated at the logic printed circuit board. The snubber
board sensing circuits send data to the logic board for factoring
into firing signal generation. The snubber board also includes an
RC network for a degree of protection against false firing of the
SCR’s due to dv/dt and MOV’s for transient protection.
5