UMTS/HSPA+ Module Series
UG89 Hardware Design
UG89_Hardware_Design 38 / 73
USB_DP
USB_DM
GND
USB_DP
USB_DM
GND
L1
Close to Module
R3
R4
Test Points
ESD Array
NM_0R
NM_0R
Minimize these stubs
Module
MCU
USB_VBUS
VDD
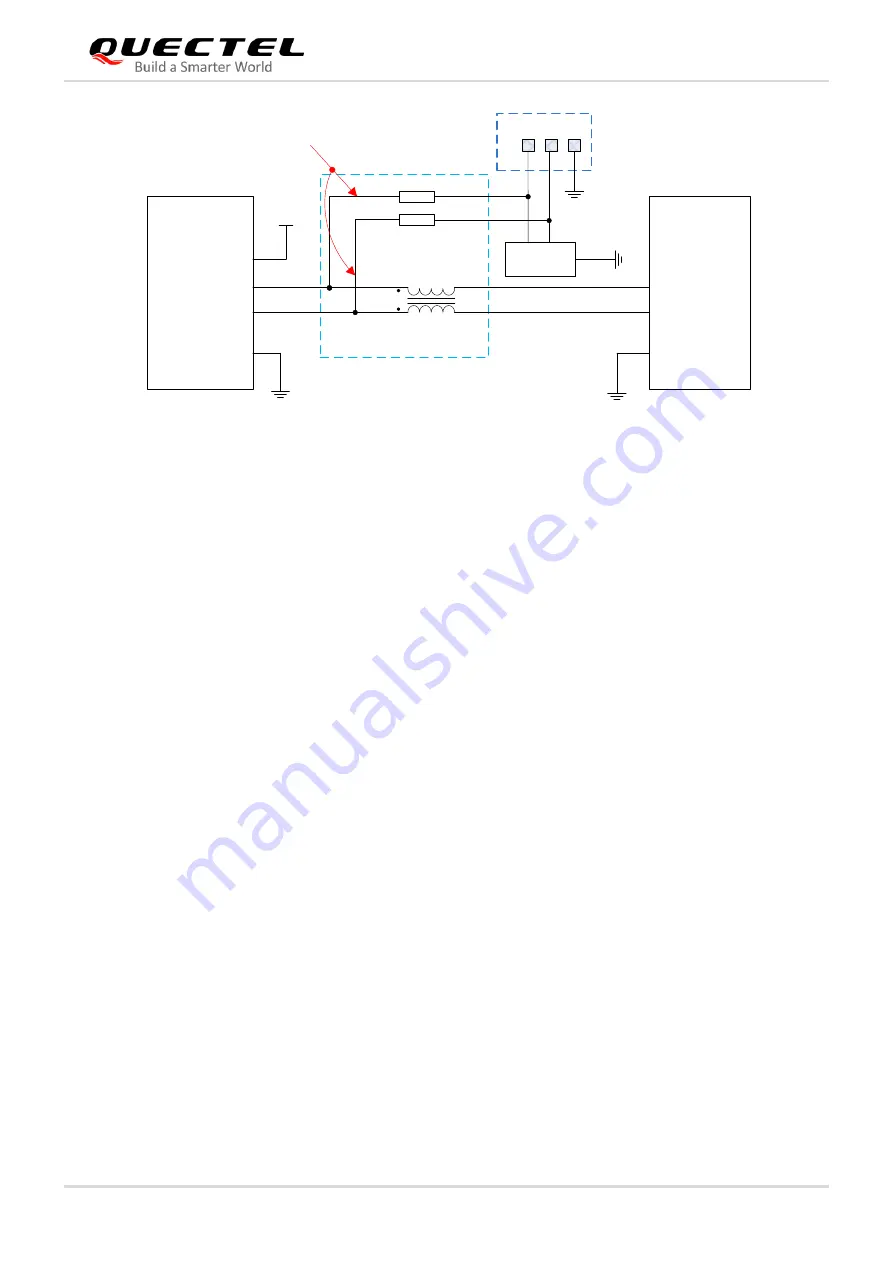
Figure 17: Reference Circuit of USB Application
A common mode choke L1 is recommended to be
added in series between the module and customer’s
MCU in order to suppress EMI spurious transmission. Meanwhile, the 0Ω resistors (R3 and R4) should be
added in series between the module and the test points so as to facilitate debugging, and the resistors are
not mounted by default. In order to ensure the integrity of the USB data line signal, L1, R3 and R4
components must be placed close to the module, and also resistors R3 and R4 should be placed close to
each other. The extra stubs of trace must be as short as possible.
The following principles should be followed when designing the USB interface, so as to meet USB 2.0
specification.
It is important to route the USB signal traces as differential pairs with total grounding. The impedance
of USB differential trace is 90
Ω.
Do not route signal traces under crystals, oscillators, magnetic devices and RF signal traces. It is
important to route the USB differential traces in inner-layer of the PCB, and surround the traces with
ground on that layer and ground planes above and below.
Please pay attention to the selection of the ESD component on the USB data line. Its parasitic
capacitance should not exceed 2pF and should be placed as close as possible to the USB interface.
3.10. ADC Interfaces
The module provides two analog-to-digital converter (ADC) interfaces.
AT+QADC=0
can be used to read
the voltage value on ADC pin. For more details about these AT commands, please refer to the
document
[2]
.
In order to improve the accuracy of ADC, the traces of ADC interfaces should be encircled by ground
traces.
















































