P300H
P300 Series Modem Installation and Operating Handbook
Page 208
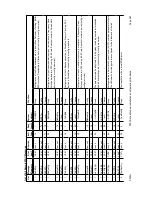
FAULT MODE SETTING
0
Default (normal) fault detection
1
ISDN Backup (<V2.14) / ISDN backup AND OQPSK Compatibility (>=V2.14)
Software <V2.14: Exactly as defined for Fault Mode 13 (but available in earlier versions).
Software >=V2.14: A combination of Fault Mode 13 (ISDN backup) AND Fault Mode 12
(OQPSK Compatibility).
2
Telenor (Receive fail Transmit Inhibit, RTI)
This additional feature allows the guaranteed shutdown of transmission from a remote
unmanned site even in the event that all M&C is lost. When enabled this remote shutdown is
accomplished by muting the signal
to
the remote destination, which will then mute its transmit
carrier whenever the `receive input signal is lost` for more than 10 seconds continuously.
Specifically:
The definition of `receive input signal is lost` includes demod unlocked, FEC sync lost, RS
sync lost, frame sync lost (if applicable), and Multiframe sync lost (if applicable).
The remote transmit will unmute when all the above alarms have been clear for 5 seconds.
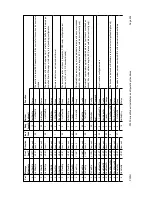
3
Max Sequential decoder gain
In normal operation at data rates of 128kbps and below, to reduce the delay through the
sequential decoder (if selected as the FEC in operation), the decoder processing memory is
shortened at the cost of slightly reduced decoder gain. This option
disables
the shortening of the
memory, and leaves the maximum memory in circuit maximising the Sequential decoder gain
(at the cost of increased processing delay). In the normal mode (when this function is not active)
the decoder memory is 4096 bits, but at receive rates of 128kbps and below this is reduced to
2048 bits, 64kbps and below 1024 bits, and 32kbps and below 512bits. This means the
maximum delay is 32ms at 128.001kbps, and stays between 32ms and 16ms right down to
16kbps, (below which, with the minimum 512bits of processing memory the delay increases
again above 32ms). The data rate used to determine the processing memory size is the receive
rate
including
any framing and Reed-Solomon overheads (as this is the output rate of the
sequential decoder). See the separate note in section 8.4 on page 146 regarding minimising the
Reed-Solomon delay.
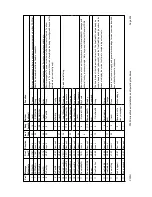
4
Slow Sweep / Poor Eb/No Acquisition
Satellite modems are one large compromise, and part of this compromise is a trade off between
poor Eb/No acquisition performance and normal Eb/No acquisition speed. The modem is
optimised for reasonably fast acquisition down to an Eb/No of 5dB, and the sweep speed is set
to match goal. This option reduces the sweep speed (and hence increases the acquisition time)
by a factor of ten, but improves the low Eb/No acquisition by approx 0.5dB. It is advisable when
using this setting to narrow the Rx sweep width (if you know the frequency of the Rx carrier to
be fairly accurate) to help speed up the acquisition while sweeping at this very slow rate.
5
Post Reed-Solomon V35 Scrambling
Not available on the P300.
6
Fast Eb/No monitoring
The raw Eb/No information the M&C reads varies significantly and so the Eb/No displayed by
the equipment is a heavily averaged to provide a steady result to display. In some
circumstances it is desirable to have a faster display of Eb/No (eg to track short duration
interruptions such as a helicopter crossing the beam), and this option disables the Eb/No
averaging providing a faster responding, but rather jittery Eb/No display.
Содержание P300 Series
Страница 21: ...P300H P300 Series Modem Installation and Operating Handbook Page 21 F BLOCK DIAGRAM ...
Страница 22: ...P300H P300 Series Modem Installation and Operating Handbook Page 22 ...
Страница 163: ...P300H P300 Series Modem Installation and Operating Handbook Page 163 8 12 4 Eb No Explanatory Diagram ...