118
Protective and Diagnostic Functions
Chapter 8-1
8-1
Protective and Diagnostic Functions
8-1-1
Fault Detection (Fatal Error)
The Inverter will detect the following faults if the Inverter or motor burns or the
internal circuitry of the Inverter malfunctions. When the Inverter detects a
fault, the fault code will be displayed on the Digital Operator, the fault contact
output will operate, and the Inverter output will be shut off causing the motor
to coast to a stop. The stopping method can be selected for some faults, and
the selected stopping method will be used with these faults. If a fault has
occurred, refer to the following table to identify and correct the cause of the
fault. Use one of the following methods to reset the fault after restarting the
Inverter. If the operation command is being input, however, the reset signal
will be ignored. Therefore, be sure to reset the fault with the operation
command turned off.
• Turn on the fault reset signal. A multi-function input (n36 to n39) must be
set to 5 (Fault Reset).
• Press the STOP/RESET Key on the Digital Operator.
• Turn the main circuit power supply off and then on again.
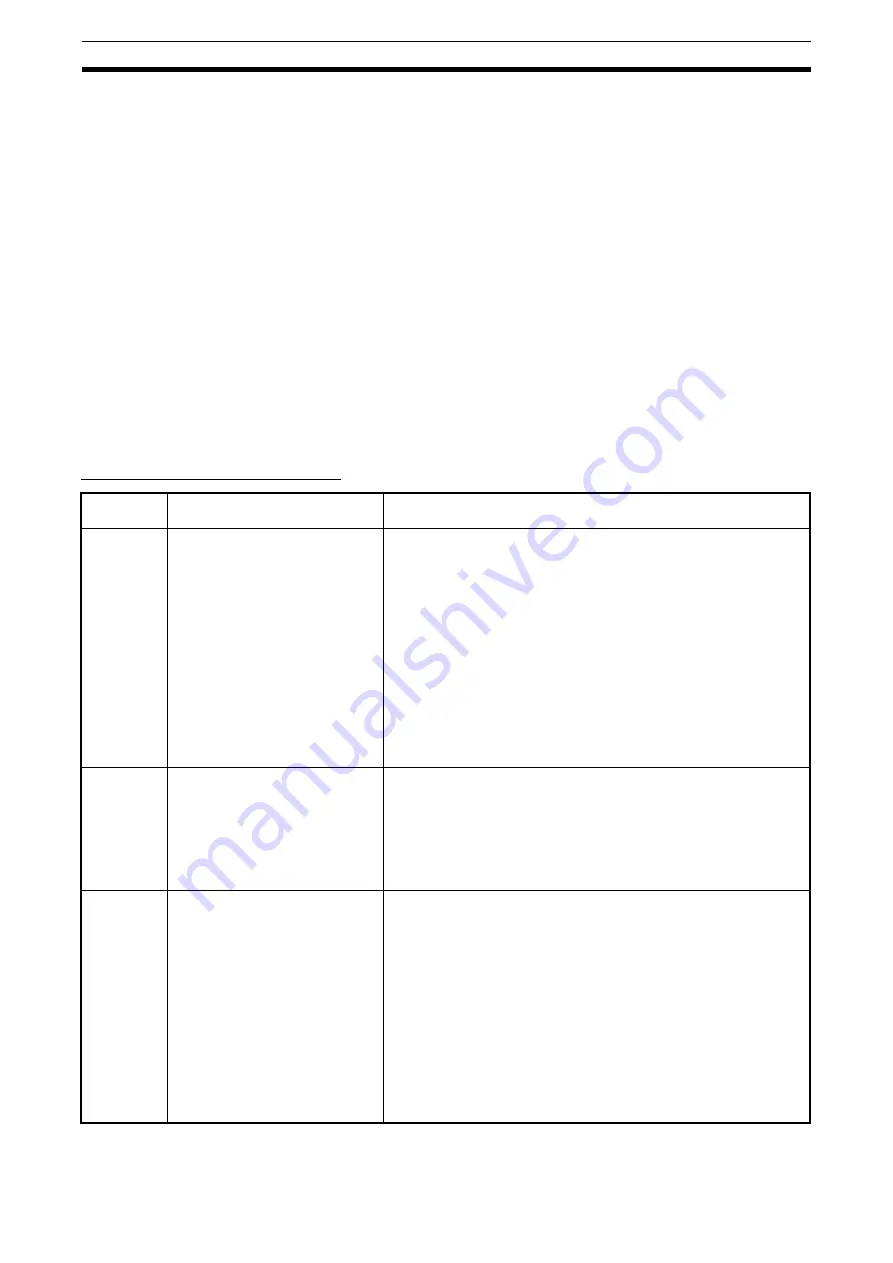
Fault Displays and Processing
Fault
display
Fault name and meaning
Probable cause and remedy
%c
Overcurrent (OC)
The Inverter output current is as
high as or higher than 200% of the
rated output current.
• A short-circuit or ground fault has occurred and at the
Inverter output.
→
Check and correct the motor power cable.
• The V/f setting is incorrect.
→
Reduce the V/f set voltage.
• The motor capacity is too large for the Inverter.
→
Reduce the motor capacity to the maximum permissible motor
capacity.
• The magnetic contactor on the output side of the Inverter has been
opened and closed.
→
Rearrange the sequence so that the magnetic contactor will not
open or close while the Inverter has current output.
• The output circuit of the Inverter is damaged.
→
Replace the Inverter.
%U
Overvoltage (OV)
The main circuit DC voltage
has reached the overvoltage
detection level
(200-V models: 410 V DC min.;
400-V models: 820 V DC min.).
• The deceleration time is too short.
→
Increase the deceleration time.
• The power supply voltage is too high.
→
Decrease the voltage so it will be within specifications.
• There is excessive regenerative energy due to overshooting
at the time of acceleration.
→
Suppress the overshooting as much as possible.
uU1
Main circuit undervoltage (UV1)
The main circuit DC voltage has
reached the undervoltage
detection level (200 V DC for the
3G3JV-A2
_
, 160 V DC for the
3G3JV-AB
_
, and 400 V DC for the
3G3JV-A4
_
).
• Power supply to the Inverter has phase loss, power
input terminal screws are loose, or the power cable is
disconnected.
→
Check the above and take necessary countermeasures.
• Incorrect power supply voltage
→
Make sure that the power supply voltage is within
specifications.
• Momentary power interruption has occurred.
→
Use the momentary power interruption compensation
(Set n47 so that the Inverter restarts after power is
restored)
→
Improve the power supply.
• The internal circuitry of the Inverter is damaged.
→
Change the Inverter.
Содержание J7 series
Страница 12: ...XII...
Страница 15: ...1 CHAPTER 1 Overview 1 1 Function 2 1 2 Nomenclature 3...
Страница 47: ...33 CHAPTER 3 Preparing for Operation and Monitoring 3 1 Nomenclature 34 3 2 Outline of Operation 35...
Страница 54: ...40 Outline of Operation Chapter 3 2...
Страница 102: ...88 Other Functions Chapter 6 7...
Страница 158: ...144 Option Specifications Chapter 9 3...
Страница 159: ...145 CHAPTER 10 List of Parameters List of Parameters 146...
Страница 172: ...158 List of Parameters Chapter 10...
Страница 173: ...159 CHAPTER 11 Using the Inverter for a Motor Using the Inverter for a Motor 160...