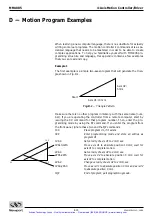
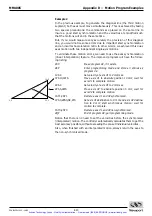
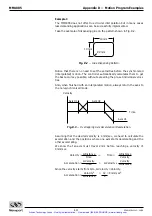
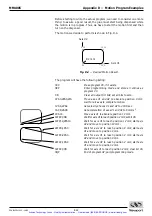
8.7
EDH0162En1040 – 06/99
B.2
IEEE-488 Function Subsets
This controller support the many GPIB function subsets, as listed bellow.
Some of the listings described subsets that the controller does not support.
C0
(Controller). The MM4005 can not control other devices.
T5
(Talker). The MM4005 becomes a Talker when the CIC (Controller In
Charge) sends its TAD (Talker Address) with the ATN (Attention) line
asserted. It ceases to be a talker when the CIC (Controller In Charge) sends
another device’s TAD (Talker Address) with ATN (Attention) asserted.
L4
(Listener). The MM4005 becomes Listener when the CIC (Controller In
Charge) sends its LAD (Listener Address) with the ATN line asserted. The
MM4005 does not have Listen Only capability.
SH1
(Source Handshake). The MM4005 can transmit multiline messages
accros the GPIB.
AH1
(Acceptor Handshake). The MM4005 can receive multiline messages
accros the GPIB.
SR1
(Service Request). The MM4005 asserts SRQ (Serial Request) line to
notify the CIC ( controller In Charge ) when it requires service.
RL0
(Remote / Local). The MM4005 does not support the GTL (Go To
Local) and LLO (Local Lock Out) functions.
PP0
(Parralel Poll). The MM4005 has no Parallel Poll capability. It does not
respond to the following interface messages: PPC, PPD, PPE and PPU. The
MM4005 does not send out a message when the ATN (Attention) and EOI
(End or Identify) line are asserted.
DC1
(Device Clear). The MM4005 responds to the DCL (Device Clear) and,
when made Listener, the SDC (Selected Device Clear) interface message.
DT0
(Device Trigger). The MM4005 does not support GET (Group Execute
Trigger) interface message.
E2
(Electrical). The MM4005 uses tristate buffers to provide optimal high-
speed data transfer.
B.3
SRQ Using
The NI488.2 User Manual for Windows from National Instruments, in the
GPIB Programming Techniques chapter describes the use of Serial Polling
as follow (page 7-5):
Serial Polling
You can use serial polling to obtain specific information from GPIB devices
when they request service. When the GPIB SRQ line is asserted, it signals
the Controller that a service request is pending. The controller must then
determine which device asserted the SRQ line and respond accordingly.
The most common method for SRQ detection and servicing is serial poll.
This section describes how you can set up your application to detect and
respond to service requests from GPIB devices.
Service Requests from IEEE-488 Devices
IEEE-488 devices request service from the GPIB Controller by asserting the
GPIB SRQ line. When the Controller acknowledge the SRQ, it serial polls
each open device on the bus to determine which device requested service.
Any device requesting service returns a status byte with bit 6 set and then
unasserts the SRQ line. Devices not requesting service return a status byte
with bit 6 cleared. Manufacturers of IEEE-488 devices use lower order bits
to communicate the reason for the service request or to summarize the
state of the device.
MM4005
Appendix B — IEEE-488 Link Characteristics
MM4005
Appendix B — IEEE-488 Link Characteristics
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com
Содержание MM4005
Страница 360: ...Section 7 Servo Tuning Artisan Technology Group Quality Instrumentation Guaranteed 888 88 SOURCE www artisantg com ...
Страница 368: ...Section 8 Appendices Artisan Technology Group Quality Instrumentation Guaranteed 888 88 SOURCE www artisantg com ...
Страница 405: ...EDH0162En1040 06 99 8 36 Artisan Technology Group Quality Instrumentation Guaranteed 888 88 SOURCE www artisantg com ...
Страница 406: ...Section 9 Index Artisan Technology Group Quality Instrumentation Guaranteed 888 88 SOURCE www artisantg com ...