1-32
|
ni.com
Chapter 1
Getting Started with the cDAQ Chassis
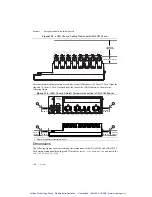
Chassis Grounding Screw
Caution
To ensure the specified EMC performance, the cDAQ chassis
must
be
connected to the grounding electrode system of your facility using the chassis ground
terminal.
The wire should be 1.31 mm
2
(16 AWG) or larger solid copper wire with a maximum length of
1.5 m (5 ft). Attach the wire to the earth ground of the facility’s power system. For more
information about earth ground connections, refer to the
Grounding for Test and Measurement
Devices
document by going to
ni.com/info
and entering the Info Code
emcground
.
Note
If you use shielded cabling to connect to a C Series module with a plastic
connector, you must attach the cable shield to the chassis grounding terminal using
1.31 mm
2
(16 AWG) or larger wire. Use shorter wire for better EMC performance.
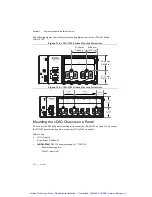
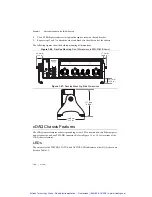
Time-Based Features
cDAQ-9185/9189 chassis feature automatic network-based synchronization with compatible
networks and 802.1AS-capable NI Linux Real-Time controllers. The SYNC logo on the chassis
front panel, shown in Figures 1-1 and 1-2, indicate that the chassis are capable of
hardware-based synchronization over a network.
The chassis can be daisy-chained to each other or connected to external networks that support
802.1AS synchronization, and all chassis timebases will be automatically synchronized. Refer
to Chapter 2,
Networking
, and the
Synchronization across a Network
section of Chapter 7,
Digital Routing, Clock Generation, and Synchronization
, for more information about supported
topologies and other technical requirements.
Network-synchronized chassis can also take advantage of time-based synchronization features
in NI-DAQmx. Certain triggers and timestamps can be specified in terms of time of day.
Time-based triggers and timestamps and multichassis tasks (spanning multiple
network-synchronized cDAQ chassis) can help simplify programming for large systems.
Time triggers and timestamps can be specified in Host Time or I/O Device Time, depending on
the needs of your application.
•
I/O Device Time
—The time the cDAQ-9185/9189 uses internally. This time is determined
by the network configuration and is shared by all 802.1AS network-synchronized devices
on your subnet.
•
Host Time
—The time on your PC or NI Linux Real-Time controller. This is usually the
current global time, and is provided by a local real-time clock or a network time protocol
(NTP) server.
NI-DAQmx automatically translates from Host Time to I/O Device Time as necessary. The
accuracy of this translation depends on the relationship between these times and can reduce the
relative accuracy of time triggers and timestamps across multiple devices. For maximum
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com