52
Advanced image processing
Histogram corrections
The histogram indicates the distribution of pixels with specific brightness or color values in the
image. Using the histogram can maximize the output of the image data. Changes made with the
histogram are also displayed on the tone curve.
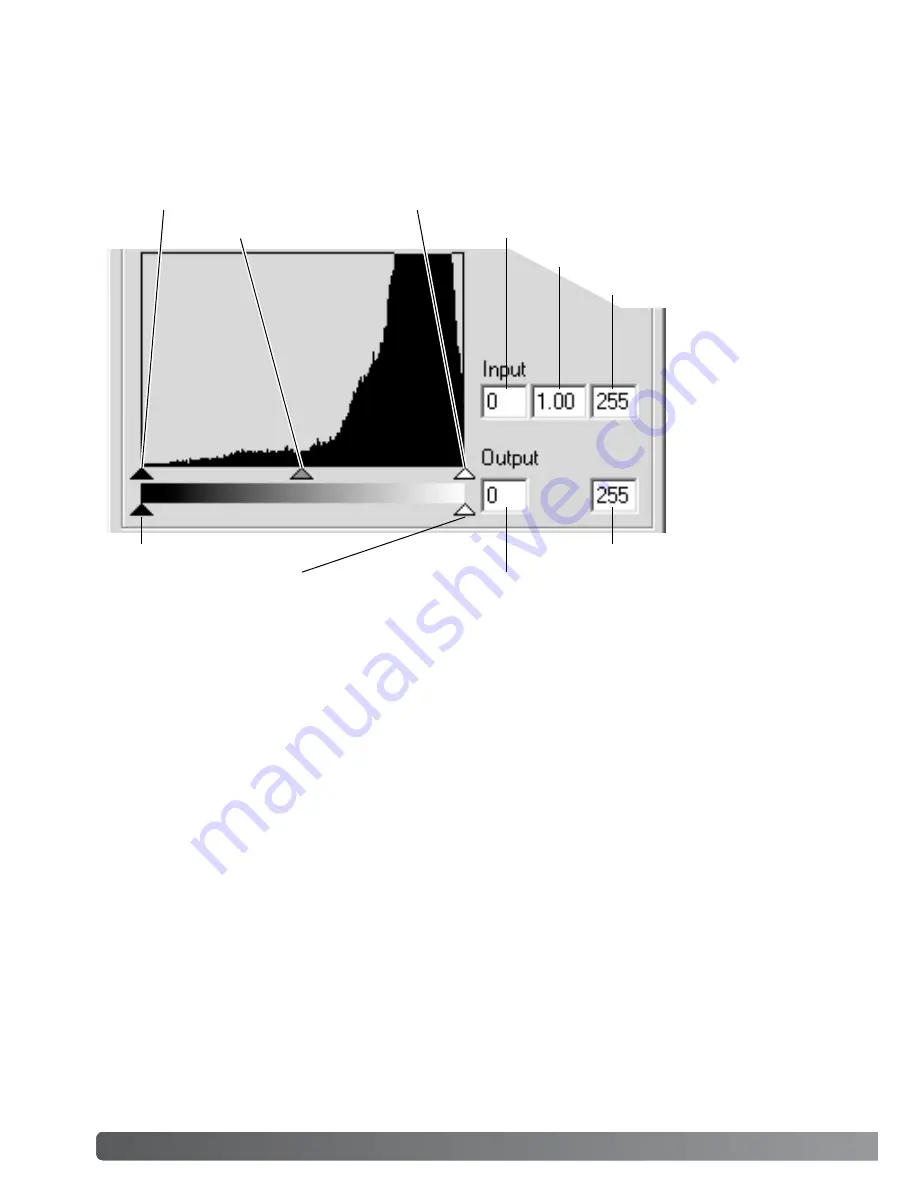
Input shadow slider
Input gamma slider
Input highlight slider
Input shadow text box
Input gamma text box
Input highlight text box
Output shadow slider
Output highlight slider
Output shadow text box
Output highlight text box
The color histograms can be displayed with the channel list box or with keyboard shortcuts. While
holding the control key (Windows) or command key (Macintosh), press 0 (zero) to display the
RGB channel, 1 to display the red channel, 2 to display the green channel, or 3 to display the blue
channel.
The histogram can be used to maximize the distribution of the pixels in the image. The highlight
level, shadow level, and gamma can be set manually with the sliders or text boxes.
The gamma slider defines the mid-tones of the image. Dragging the gamma slider to the right will
darken the image, and dragging it to the left will brighten it. Similar to the tone-curve correction
described on page 50, the gamma slider allows the brightness of the image to be adjusted with-
out loosing image information.
The input highlight slider sets the white level. As the slider is moved to the left, an apparent
increase in contrast can be seen in the displayed image. All pixels to the right of the slider are set
to 255 and any image detail they may contain will be lost. This can be an important tool for
improving copy images of text on a white background. Uneven illumination, or faded or stained
paper can be distracting when copying text or line art. By adjusting the white level, the imperfec-
tions of the white background can be eliminated leaving only the darker text visible.