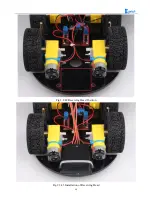
95
if
(
ps2x
.
Button
(
PSB_L1
))
/ * If the received signal is PSB_L1, execute the command in
{}. * /
{
vb
=
ps2x
.
Analog
(
PSS_LY
);
/ * Read the value of PSS_LY, that is, the joystick value,
and assign this value to the variable vb. The joystick range is 0-255. When you press
L1, you can toggle the joystick to generate the corresponding value. If L1 is not
pressed, dial rocker will not produce the corresponding value. Because PWM is also 0-
255, so we directly convert the value generated by the joystick into PWM, so as to
control the motor speed. Experimental results are: Press the L1, dial the left rocker,
the car can be accelerated or slowed down in the process of progress. * /
analogWrite
(
M1
,
0
);
analogWrite
(
E1
,
vb
);
//the speed value of motorA is vb
analogWrite
(
M2
,
0
);
analogWrite
(
E2
,
vb
);
//the speed value of motorB is vb
}
if
(
ps2x
.
Button
(
PSB_R1
))
/ * If the received signal is PSB_R1, execute the command in
{}. * /
{
KK
=
ps2x
.
Analog
(
PSS_RY
);
/ * Read the value of PSS_RY, ie the joystick value, and
assign this value to the variable kk. The joystick range is 0-255. When you press R1,
you can toggle the joystick to generate the corresponding value. If R1 is not pressed,
dial rocker will not produce the corresponding value. Because PWM is also 0-255, so we
directly convert the value generated by the joystick into PWM, so as to control the
motor speed. The experimental result is: press R1, dial the right joystick, the car can
be accelerated or decelerated in the process of receding. * /
analogWrite
(
M1
,
KK
);
//the speed value of motorA is kk
analogWrite
(
E1
,
0
);
analogWrite
(
M2
,
KK
);
//the speed value of motorA is kk
analogWrite
(
E2
,
0
);
}
delay
(
50
);
}
In the above program, we used a lot of buttons, but they are all showed in code form and no details to
any keys. Now we will know about these buttons, if you download the above program directly to the
development board, you can control the car with PS2 handle in accordance with the instructions below as
shown in Fig.3.2.46. Of course, we encourage users to write programs, set keys according to their own ideas,
so the development of the car will be very meaningful.
Содержание Hummer-Bot
Страница 1: ...Hummer Bot Instruction Manual Github https github com keywish keywish hummer bot...
Страница 7: ...4...
Страница 8: ...5...
Страница 9: ...6...
Страница 10: ...7...
Страница 13: ...10 Fig 2 2 Several commonly usedArduino...
Страница 15: ...12 After the completion as shown...
Страница 16: ...13 The second step is to Welding wire on the motor...
Страница 17: ...14 After the completion as shown...
Страница 19: ...16 Fig 3 1 3 Diagram of Aluminum Alloy Bracket Installation...
Страница 20: ...17 Fig 3 1 4 Diagram of Motor Installation Fig 3 1 5 Fixing Screw for Motor...
Страница 24: ...21 Fig 3 1 10 Diagram of Wheel Installation Fig 3 1 10 Diagram of Wheel Screw Fixation...
Страница 29: ...26 Fig 3 1 15 Diagram of Tracing Module Installation...
Страница 30: ...27 Fig 3 1 16 Diagram of Screw Brackets Fig 3 1 17 The Back of Complete Installation...
Страница 32: ...29 First install the screws on the UNO After the completion as shown...
Страница 33: ...30 Then install UNO on acrylic plates Fig 3 1 20 Diagram of Arduino Mainboard and Battery Box Installation...
Страница 43: ...40 Fig 3 1 33 Diagram of Wires Arrangement Fig3 1 34 the Effect of Whole Assembly...
Страница 56: ...53 Fig 3 2 11 Diagram of Data with Obstacles Fig 3 2 12 Diagram of Data without Obstacles...
Страница 69: ...66 Fig 3 2 22 Diagram of Steering Gear Fig 3 2 23 Composition of Steering Gear...
Страница 93: ...90 Fig 3 2 42 Receiving Head Position Fig 2 3 43 Installation of Receiving Head...