150
exercised successfully. Configuring this value to
Failure
generates an audit entry each time that a user
right is exercised unsuccessfully. Audits are not generated when the following user rights are
exercised, even if the
Audit privilege use
settings is configured to
Success
or
Failure
. This is because
auditing these user rights generates many events in the security log, which may constrain the
performance of the NAS and other server systems. However, CC security recommends modifying this
setting to
Success
Failure
. To audit the following excluded rights, administrators must enable the
Audit: Audit the use of Backup and Restore privilege
security option in Group Policy:
•
Bypass traverse checking
•
Debug programs
•
Create a token object
•
Replace process level token
•
Generate security audits
•
Back up files and directories
•
Restore files and directories
Warning
: Enabling privilege auditing generates a very large number of event records. For this
reason, each security environment defined in this guide has unique recommendations for these
settings. Failed use of a user right is an indicator of a general network problem and often can be a
sign of an attempted security breach. Corporations should set the
Audit privilege use
setting to
Enable
only if there is a specific business reason to do so.
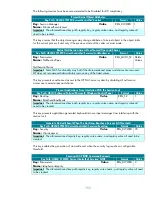
Audit Process Tracking
Member Server Default
Legacy Client
Enterprise Client
High Security Client
No Auditing
Success Failure
Success Failure
Success Failure
This Audit policy value can be configured in the Domain Group Policy section of Windows Server
2003 at the following location:
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Audit Policy
The
Audit process tracking
setting determines whether to audit detailed tracking information for events
such as program activation, process exit, handle duplication, and indirect object access. Configuring
this setting to
Success
generates an audit entry each time the process being tracked succeeds.
Configuring this setting to
Failure
generates an audit entry each time the process being tracked fails.
Enabling
Audit process tracking
will generate a large number of events, so typically it is set to
No
Auditing
. However, these settings can provide a great benefit during an incident response from the
detailed log of the processes started and the time when they were launched. As such, for CC security
compliancy, administrators should modify this setting to
Success Failure.
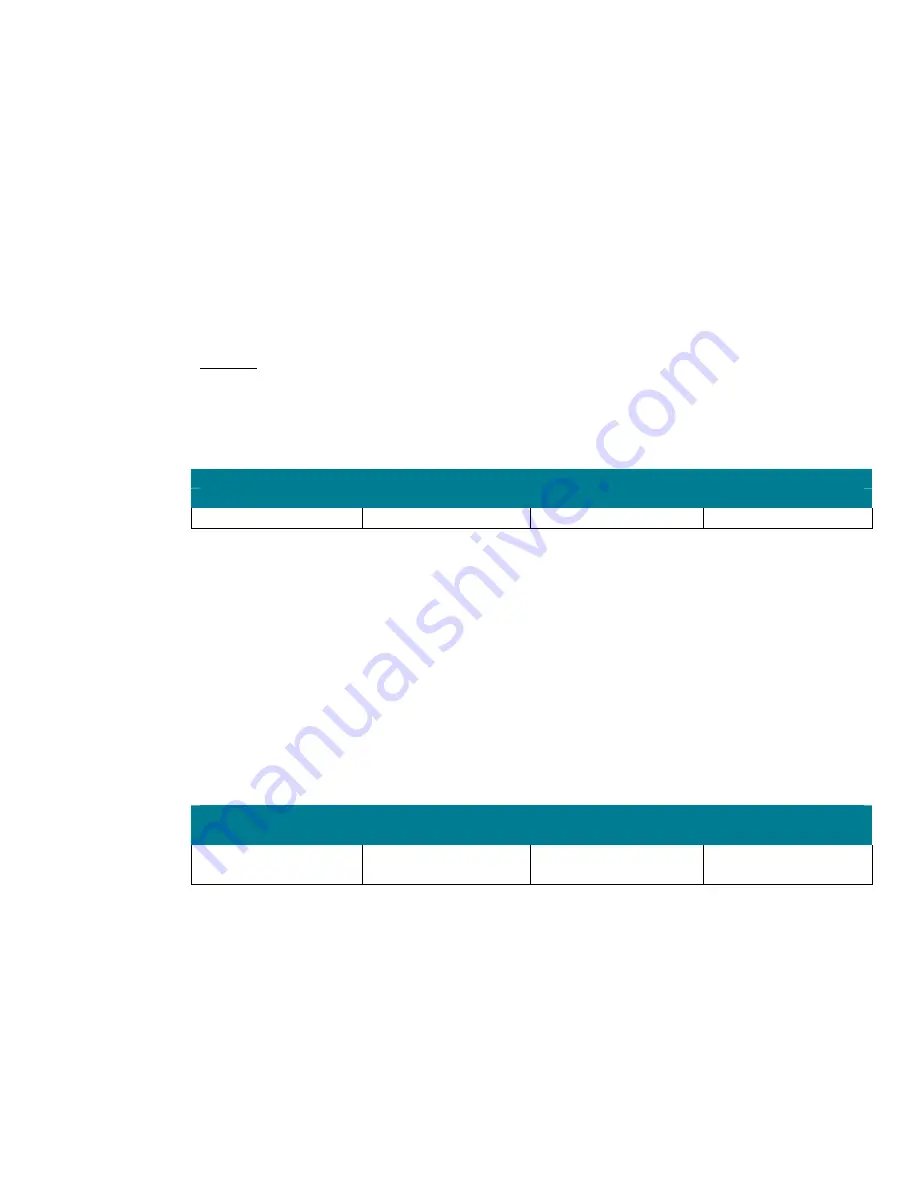
Audit: Audit the access of global system objects
Member Server Default
Legacy Client
Enterprise Client
High Security Client
Disabled
Enabled
Enabled
Enabled
This Security Option setting can be configured in Windows Server 2003 at the following location
within the Group Policy Object Editor:
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Security Options
The
Audit: Audit the access of global system objects
security option setting audits the access of global
system objects when it is in effect. If both the
Audit: Audit the access of global system objects
and the
Audit object access audit policy
settings are enabled, a large number of audit events will be
generated. For CC security compliancy, this setting is configured to
Enabled
within all three
environments defined in this guide.