27
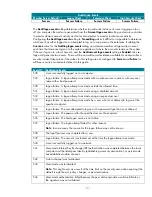
Audit System Events
Member Server Default
Legacy Client
Enterprise Client
High Security Client
No Auditing
Success
Success
Success
The
Audit system events
setting determines whether to audit when a user restarts or shuts down a
computer or when an event occurs that affects either the system security or the security log.
Configuring this setting to
Success
generates an audit entry when a system event is executed
successfully. Configuring this setting to
Failure
generates an audit entry when a system event is
attempted unsuccessfully. The table below includes some of the most useful successful events for this
category.
Event ID
Event Description
512
Windows is starting up.
513
Windows is shutting down.
514
An authentication package was loaded by the Local Security Authority.
515
A trusted logon process has registered with the Local Security Authority.
516
Internal resources allocated for the queuing of security event messages have been
exhausted, leading to the loss of some security event messages.
517
The audit log was cleared.
518
A notification package was loaded by the Security Accounts Manager.
519
A process is using an invalid local procedure call (LPC) port in an attempt to impersonate
a client and reply or read from or write to a client address space.
520
The system time was changed.
Note:
This audit normally appears twice.
2.8.2
User Rights Assignments
User Rights Assignments determine which users or groups have logon rights or privileges on the
computers on the network. Logon rights and privileges govern the rights that users have on the target
system. They are used to grant the right to perform certain actions, such as logging on from the
network or locally, as well as administrative tasks, such as generating new logon tokens. User rights
assignment settings can be configured in Windows Server 2003 in the following location within the
Group Policy Object Editor:
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Assignment
The default User Rights Assignments are different between the various types of servers in the network.
For example, Windows Server 2003 contains the following differences in User Rights Assignments
with built-in groups between member servers and domain controllers. Similar built-in groups between
member servers and domain controllers are not documented in the list that follows.