Rev. 1.00
146
September 11, 2018
Rev. 1.00
147
September 11, 2018
HT45F4050
A/D NFC Flash MCU
HT45F4050
A/D NFC Flash MCU
I
2
C Bus Communication
Communication on the I
2
C bus requires four separate steps, a START signal, a slave device address
transmission, a data transmission and finally a STOP signal. When a START signal is placed on
the I
2
C bus, all devices on the bus will receive this signal and be notified of the imminent arrival of
data on the bus. The first seven bits of the data will be the slave address with the first bit being the
MSB. If the address of the slave device matches that of the transmitted address, the HAAS bit in
the SIMC1 register will be set and an SIM interrupt will be generated. After entering the interrupt
service routine, the slave device must first check the condition of the HAAS and SIMTOF bits
to
determine whether the interrupt source originates from an address match or from the completion of
an 8-bit data transfer completion or from the I
2
C bus time-out occurrence. During a data transfer,
note that after the 7-bit slave address has been transmitted, the following bit, which is the 8th bit, is
the read/write bit whose value will be placed in the SRW bit. This bit will be checked by the slave
device to determine whether to go into transmit or receive mode. Before any transfer of data to or
from the I
2
C bus, the microcontroller must initialise the bus, the following are steps to achieve this:
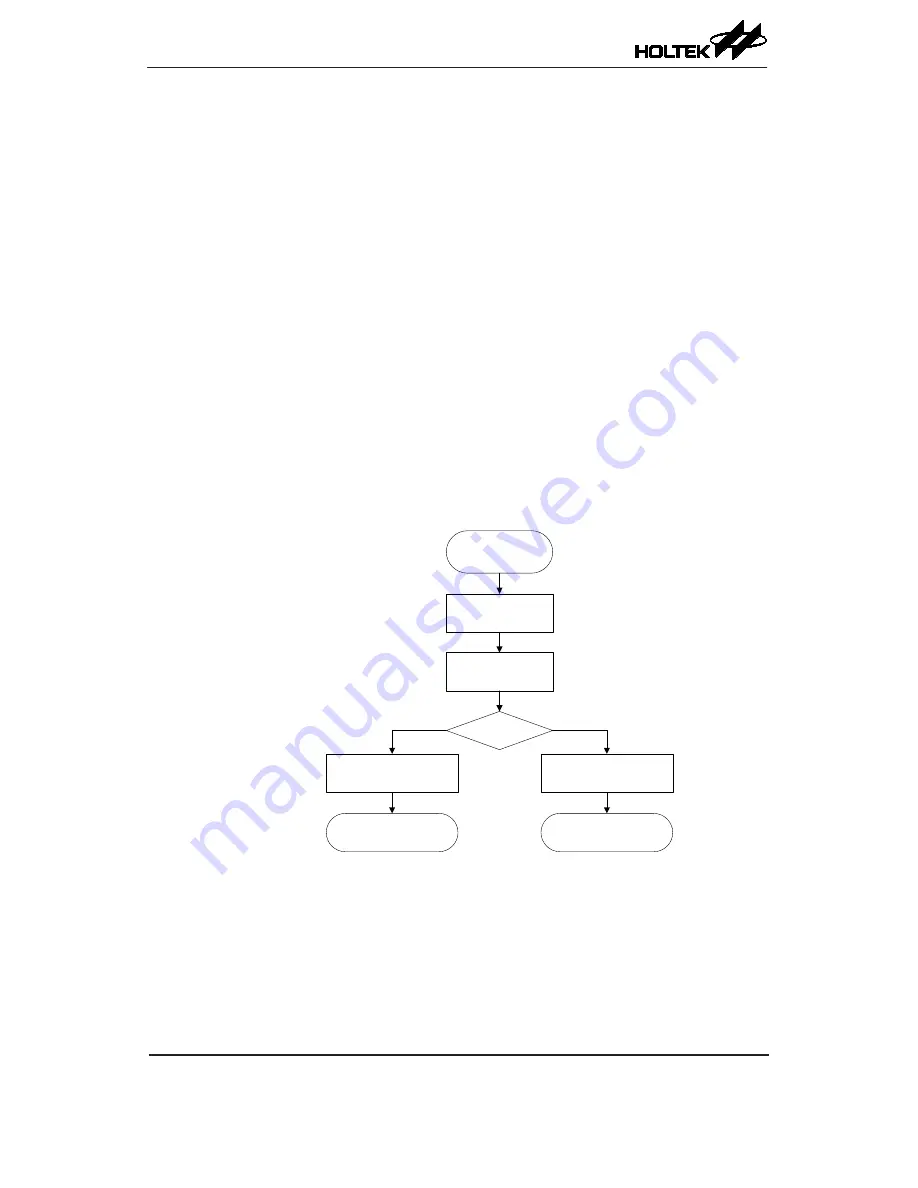
• Step 1
Set the SIM2~SIM0 and SIMEN bits in the SIMC0 register to
"
110
" and "1" respectively
to
enable the I
2
C bus.
• Step 2
Write the slave address of the device to the I
2
C bus address register SIMA.
• Step 3
Set the SIME interrupt enable bit of the interrupt control register to enable the SIM interrupt.
Start
SET SIM[2:0]=110
SET SIMEN
Write Slave
Address to SIMA
I
2
C Bus
Interrupt=?
CLR SIME
Poll SIMF to decide
when to go to I
2
C Bus ISR
SET SIME
Wait for Interrupt
Go to Main Program
Go to Main Program
Yes
No
I
2
C Bus Initialisation Flow Chart
















































