2—Functional Design
Intraplex NetXpress IP Multiplexer
Version 3.05
GatesAir, Inc.
2-3
Intraplex Products
2.1.6.2 Disable WAN Link Redundancy
If you are going to disable WAN link redundancy, you must clear the
Use
LAN
as
Redundant
WAN
Link
check box on the
WAN
Interface
Configuration
screen (Section 4.4.4.1 –
Network Interface
Configuration
) and Trunking must be disabled on the switch ports. We also recommend that the LAN
cable be disconnected so that the switch releases any cached MAC addresses.
2.1.7
IGMP Multicast
The NetXpress system interoperates with Multicast Routers using the Internet Group Management
Protocol (IGMP). The IGMP Multicast mode involves transmission to specific hosts through IGMP
routers. This scheme allows you to route specific packets onto specific segments, thereby segregating
unwanted traffic from narrow segments.
The NetXpress system supports IGMP v2 messages. When a “receive” multicast stream is configured,
it sends out IGMP membership reports. Similarly, when the multicast streams are deleted, the
NetXpress system sends out an IGMP Leave message and also responds to the membership queries
from the router. It supports the proprietary IGMP statistics MIB to account for all incoming and
outgoing messages.
2.2 Streams
The NetXpress IP multiplexer uses packet streaming to transport audio, voice, data, and video signals.
2.2.1
Stream Types
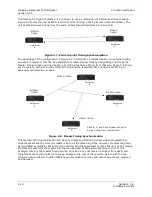
2.2.1.1 Unidirectional
versus Bidirectional
Packet streams can be unidirectional or bidirectional. In other words, streams can travel in one
direction (transmitted or received) or two directions (transmitted and received). The NetXpress
system supports both unidirectional and bidirectional packet streaming.
Most circuit types, such as voice and two-way data circuits, are bidirectional, or full-duplex. Full-
duplex circuits require identical full-duplex (transmit/receive) channel modules at both ends of the
channel they occupy within a system. Other circuit types, such as program audio channels, are
unidirectional (simplex). They always have a transmitter module at one end and a receiver module at
the other. Most bidirectional (full-duplex) channel modules can also be set up to operate in a
unidirectional (simplex) mode.
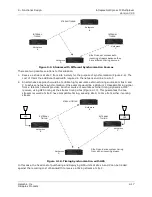
2.2.1.2 Unicast versus Multicast
Packet streams can also be classified as unicast or multicast. Unicast describes the transmission of a
piece of information (a packet stream in this case) from one point to another point. Unicast transfer
mode is still the predominant form of transmission on LANs and within the Internet. Examples of
standard unicast applications include HTTP, SMTP, FTP, and Telnet.
Multicast describes communication where a piece of information is sent from one or more points to a
set of other points (a multicast group address). There may be one or more senders and the
information is sent to a set of receivers (there may be no receiver or any number of receivers). With
multicasting, the same packet is delivered simultaneously to a group of clients. Multicast applications
must use the UDP (User Datagram Protocol) transport protocol, since TCP (Transmission Control
Protocol) only supports the unicast mode.
Most circuits provided by Intraplex multiplexer systems are unicast, including those provided with the
NetXpress system. However, several types of channel modules can be configured for point-to-
multipoint operation (multicast). For example, a single program audio transmitter module and several
program audio receiver modules can be set up in a point-to-multipoint or “broadcast” circuit
Содержание Intraplex NetXpress
Страница 2: ......
Страница 54: ...No header here 3 16 GatesAir Inc Intraplex Products This page is left blank intentionally...
Страница 146: ...No header here 4 92 GatesAir Inc Intraplex Products This page is left blank intentionally...
Страница 154: ...No header here 6 4 GatesAir Inc Intraplex Products This page is left blank intentionally...
Страница 163: ...No header here GatesAir Inc 7 9 Intraplex Products This page is left blank intentionally...